More actions
m 1 revision imported |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Creative work in which pictures and text convey information}} | |||
[[File:Little Nemo 1906-08-19.jpg|thumb| | {{redirect|Comic}} | ||
{{redirect|Comic art|the magazine|Comic Art{{!}}''Comic Art''}} | |||
{{good article}} | |||
{{Use shortened footnotes|date=June 2022}} | |||
[[File:Little Nemo 1906-08-19.jpg|upright=1.25|thumb|[[Little Nemo]], August 19, 1906 strip]] | |||
{{Comics navbar}} | |||
{{not a typo|'''Comics''' are}} a [[Media (communication)|medium]] used to express ideas with images, often combined with text or other visual information. It typically {{not a typo|takes}} the form of a sequence of [[Panel (comics)|panels]] of images. Textual devices such as [[speech balloon]]s, [[Glossary of comics terminology#Caption|captions]], and [[onomatopoeia]] can indicate dialogue, narration, sound effects, or other information. There is no consensus among theorists and historians on a definition of '''comics'''; some emphasize the combination of images and text, some sequentiality or other image relations, and others historical aspects such as mass reproduction or the use of recurring characters. [[Cartoonist|Cartooning]] and other forms of [[illustration]] are the most common means of image-making in comics. [[Photo comics]] is a form that uses photographic images. Common forms include [[comic strip]]s, [[Political cartoon|editorial]] and [[gag cartoon]]s, and [[comic book]]s. Since the late 20th century, bound volumes such as [[graphic novel]]s, [[Bande dessinée#Formats|comic albums]], and {{transl|ja|[[tankōbon]]}} have become increasingly common, along with [[webcomic]]s as well as scientific/medical comics.<ref name="pmid37980636">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lombardo P, Nairz K, Boehm I |title=Why mild contrast medium-induced reactions are sometimes over-treated and moderate/severe reactions of internal organs are undertreated: a summary based on RadioComics |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=14 |issue=1 |pages=196 |year=2023 |pmid=37980636 |doi=10.1186/s13244-023-01554-y|doi-access=free |pmc=10657911 }}</ref> | |||
== ''' | The [[history of comics]] has followed different paths in different cultures. Scholars have posited a pre-history as far back as the [[Lascaux]] cave paintings. By the mid-20th century, comics flourished, particularly in the [[History of American comics|United States]], western Europe (especially [[Bande dessinée|France and Belgium]]), and [[Manga|Japan]]. The history of [[European comics]] is often traced to [[Rodolphe Töpffer]]'s cartoon strips of the 1830s, while [[Wilhelm Busch]] and his [[Max and Moritz]] also had a global impact from 1865 on,<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.thegermanprofessor.com/max-und-moritz/ | title=8 Things about Max und Moritz | date=30 March 2015 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.dw.com/en/max-and-moritz-how-germanys-naughtiest-boys-rose-to-global-fame/a-18808584 | title=Max and Moritz: How Germany's naughtiest boys rose to fame – DW – 10/27/2015 | website=[[Deutsche Welle]] }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.outdooractive.com/en/story/harz/the-original-story-of-max-and-moritz/28754663/ | title=The original story of Max and Moritz }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.toonsmag.com/max-and-moritz/ | title=Max and Moritz: A Tale of Mischief and Influence - Toons Mag | date=8 October 2023 }}</ref> and became popular following the success in the 1930s of strips and books such as ''[[The Adventures of Tintin]]''. [[History of American comics|American comics]] emerged as a [[Mass media|mass medium]] in the early 20th century with the advent of newspaper comic strips; magazine-style [[American comic book|comic books]] followed in the 1930s, the [[superhero]] genre became prominent after [[Superman]] appeared in 1938. [[History of manga|Histories of Japanese comics and cartooning]] (''{{transl|ja|[[manga]]}}'') propose origins as early as the 12th century. Japanese comics are generally held separate from the evolution of Euro-American comics, and Western comic art probably originated in 17th-century Italy.<ref>[https://books.google.com/books?id=3bfPAgAAQBAJ Gothic in Comics and Graphic Novels by Julia Round page 24 and 25]</ref> Modern Japanese comic strips emerged in the early 20th century, and the output of comic magazines and books rapidly expanded in the post-World War II era (1945)– with the popularity of cartoonists such as [[Osamu Tezuka]]. {{not a typo|Comics has}} had a [[Low culture|lowbrow]] reputation for much of their history, but towards the end of the 20th century, they began to find greater acceptance with the public and academics. | ||
The English term ''comics'' is used as a [[Noun|singular noun]] when it refers to the medium itself (e.g. "''Comics is'' a visual art form."), but becomes plural when referring to works collectively (e.g. "''Comics are'' popular reading material.").{{TOC limit|3}} | |||
The comics may be further adapted to animations (anime), dramas, TV shows, movies. | |||
== | ==Origins and traditions== | ||
{{main|History of comics|List of comics by country}} | |||
== ''' | <gallery caption="Examples of early comics" mode="packed" heights="180"> | ||
Manga Hokusai.jpg|''[[Hokusai Manga|Manga]]''<br />[[Hokusai]], early 19th century<!-- have to find the date for this example --> | |||
Toepffer Cryptogame 13.png|{{lang|fr|Histoire de Monsieur Cryptogame}}<br />[[Rodolphe Töpffer]], 1830 | |||
Max_und_Moritz_tinted_21.png|[[Max and Moritz]]''<br />[[Wilhelm Busch]], 1865 | |||
AllySloper.jpg|[[Ally Sloper]] in ''Some of the Mysteries of Loan and Discount''<br />[[Charles Henry Ross]], 1867 | |||
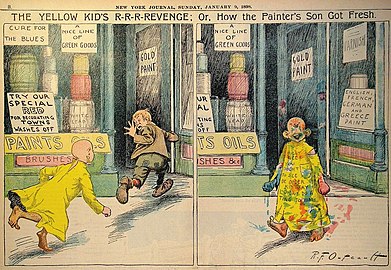
Yellow Kid 1898-01-09.jpg|''[[The Yellow Kid]]''<br />[[Richard F. Outcault|R. F. Outcault]], 1898 | |||
</gallery> | |||
The European, American, and Japanese comics traditions have followed different paths.{{sfn|Couch|2000}} Europeans have seen their tradition as beginning with the Swiss [[Rodolphe Töpffer]] from as early as 1469 and Americans have seen the origin of theirs in [[Richard F. Outcault]]'s 1890s newspaper strip ''[[The Yellow Kid]]'', though many Americans have come to recognize Töpffer's precedence. [[Wilhelm Busch]] directly influenced [[Rudolph Dirks]] and his [[Katzenjammer Kids]].<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.thegermanprofessor.com/max-und-moritz/ | title=8 Things about Max und Moritz | date=30 March 2015 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.dw.com/en/max-and-moritz-how-germanys-naughtiest-boys-rose-to-global-fame/a-18808584 | title=Max and Moritz: How Germany's naughtiest boys rose to fame – DW – 10/27/2015 | website=[[Deutsche Welle]] }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.outdooractive.com/en/story/harz/the-original-story-of-max-and-moritz/28754663/ | title=The original story of Max and Moritz }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.toonsmag.com/max-and-moritz/ | title=Max and Moritz: A Tale of Mischief and Influence - Toons Mag | date=8 October 2023 }}</ref>{{sfnm|1a1=Gabilliet|1y=2010|1p=xiv|2a1=Beerbohm|2y=2003|3a1=Sabin|3y=2005|3p=186|4a1=Rowland|4y=1990|4p=13}} Japan has a long history of satirical cartoons and comics leading up to the World War II era. The [[ukiyo-e]] artist [[Hokusai]] popularized the Japanese term for comics and cartooning, ''{{transl|ja|[[manga]]}}'', in the early 19th century.{{sfnm|1a1=Petersen|1y=2010|1p=41|2a1=Power|2y=2009|2p=24|3a1=Gravett|3y=2004|3p=9}} In the 1930s [[Harry "A" Chesler]] started a comics studio, which eventually at its height employed 40 artists working for 50 different publishers who helped make the comics medium flourish in "the Golden Age of Comics" after World War II.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/1976/09/12/archives/the-funnies-can-be-serious.html|title=The 'Funnies'|last=Ewing|first=Emma Mai|date=1976-09-12|work=The New York Times|access-date=2019-03-05|language=en-US|issn=0362-4331|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181128075857/https://www.nytimes.com/1976/09/12/archives/the-funnies-can-be-serious.html|archive-date=2018-11-28|url-status=live}}</ref> In the post-war era modern Japanese comics began to flourish when [[Osamu Tezuka]] produced a prolific body of work.{{sfnm|1a1=Couch|1y=2000|2a1=Petersen|2y=2010|2p=175}} Towards the close of the 20th century, these three traditions converged in a trend towards book-length comics: the [[comic album]] in Europe, the {{transl|ja|[[tankōbon]]}}{{efn|{{nihongo|tankōbon|単行本|extra=translation close to "independently appearing book"}}}} in Japan, and the [[graphic novel]] in the English-speaking countries.{{sfn|Couch|2000}} | |||
== | Outside of these genealogies, comics theorists and historians have seen precedents for comics in the [[Lascaux|Lascaux cave paintings]]{{sfnm|1a1=Gabilliet|1y=2010|1p=xiv|2a1=Barker|2y=1989|2p=6|3a1=Groensteen|3y=2014|4a1=Grove|4y=2010|4p=59|5a1=Beaty|5y=2012|p=32|6a1=Jobs|6y=2012|6p=98}} in France (some of which appear to be chronological sequences of images), [[Egyptian hieroglyphs]], [[Trajan's Column]] in Rome,{{sfn|Gabilliet|2010|p=xiv}} the 11th-century Norman [[Bayeux Tapestry]],{{sfnm|1a1=Gabilliet|1y=2010|1p=xiv|2a1=Beaty|2y=2012|2p=61|3a1=Grove|3y=2010|3pp=16, 21, 59}} the 1370 {{lang|fr|[[bois Protat]]}} woodcut, the 15th-century {{lang|la|[[Ars moriendi]]}} and [[block book]]s, Michelangelo's ''[[The Last Judgment (Michelangelo)|The Last Judgment]]'' in the Sistine Chapel,{{sfn|Gabilliet|2010|p=xiv}} and [[William Hogarth]]'s 18th-century sequential engravings,{{sfn|Grove|2010|p=79}} amongst others.{{sfn|Gabilliet|2010|p=xiv}}{{efn|David Kunzle has compiled extensive collections of these and other proto-comics in his ''The Early Comic Strip'' (1973) and ''The History of the Comic Strip'' (1990).{{sfn|Beaty|2012|p=62}} }} | ||
< | |||
[[Category:Comics]] | {{Panorama | ||
|image = File:Tapisserie de Bayeux 31109.jpg | |||
|height = 85 | |||
|alt = An extremely long embroidered cloth depicting events leading to the Norman conquest of England. | |||
|caption = Theorists debate whether the [[Bayeux Tapestry]] is a precursor to comics. | |||
}} | |||
===English-language comics=== | |||
[[File:An angry snarl between friendly relations (BM 1902,1011.9702).jpg|thumb|300px|"An angry snarl between friendly relations" - Satirical print on the politics around the [[Caroline Affair]] (1840–1841)]] | |||
{{multiple image | |||
| width = 180 | |||
| footer = ''The Upside Downs of Little Lady Lovekins and Old Man Muffaroo'', comics by Gustave Verbeek containing [[reversible figure]]s and [[ambigram]] sentences (March 1904). | |||
| image1 = Ambigrams by Gustave Verbeek (1904) - comics The Upside Downs of Little Lady Lovekins and Old Man Muffaroo - At the house of the writing pig.jpg | |||
| caption1 = ''At the house of the writing pig''. | |||
}} | |||
{{main|British comics|History of American comics|American comic book}} | |||
Illustrated humour periodicals were popular in 19th-century Britain, the earliest of which was the short-lived ''[[The Glasgow Looking Glass]]'' in 1825.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Dempster |first1=Michael |title=Glasgow Looking Glass |url=https://wee-windaes.nls.uk/glasgow-looking-glass/ |website=Wee Windaes |publisher=National Library of Scotland |access-date=20 June 2022}}</ref> The most popular was ''[[Punch (magazine)|Punch]]'',{{sfn|Clark|Clark|1991|p=17}} which popularized the term ''cartoon'' for its humorous caricatures.{{sfn|Harvey|2001|p=77}} On occasion the cartoons in these magazines appeared in sequences;{{sfn|Clark|Clark|1991|p=17}} the character [[Ally Sloper]] featured in the earliest serialized comic strip when the character began to feature in its own weekly magazine in 1884.{{sfn|Meskin|Cook|2012|p=xxii}} | |||
American comics developed out of such magazines as ''[[Puck (magazine)|Puck]]'', ''[[Judge (magazine)|Judge]]'', and ''[[Life (magazine)|Life]]''. The success of illustrated humour supplements in the ''[[New York World]]'' and later the ''[[New York American]]'', particularly Outcault's ''The Yellow Kid'', led to the development of newspaper comic strips. Early [[Sunday comics|Sunday strips]] were full-page{{sfn|Nordling|1995|p=123}} and often in colour. Between 1896 and 1901 cartoonists experimented with sequentiality, movement, and speech balloons.{{sfn|Gordon|2002|p=35}} An example is [[Gustave Verbeek]], who wrote his comic series "The UpsideDowns of Old Man Muffaroo and Little Lady Lovekins" between 1903 and 1905. These comics were made in such a way that one could read the 6-panel comic, flip the book and keep reading. He made 64 such comics in total. In 2012, a remake of a selection of the comics was made by Marcus Ivarsson in the book 'In Uppåner med Lilla Lisen & Gamle Muppen'. ({{ISBN|978-91-7089-524-1}}) | |||
{{wide image | |||
|1 = Mr. A. Mutt Starts in to Play the Races 1907.jpg | |||
|2 = 600px | |||
|3 = [[Bud Fisher]]'s ''[[Mutt and Jeff]]'' (1907–1982) was the first successful daily comic strip (1907).<!-- what's the date?!? --> | |||
|alt = Five-panel comic strip.}} | |||
Shorter, black-and-white daily strips began to appear early in the 20th century, and became established in newspapers after the success in 1907 of [[Bud Fisher]]'s ''[[Mutt and Jeff]]''.{{sfn|Harvey|1994|p=11}} In Britain, the [[Amalgamated Press]] established a popular style of a sequence of images with text beneath them, including ''[[Illustrated Chips]]'' and ''[[Comic Cuts]]''.{{sfn|Bramlett|Cook|Meskin|2016|p=45}} Humour strips predominated at first, and in the 1920s and 1930s strips with continuing stories in genres such as adventure and drama also became popular.{{sfn|Harvey|1994|p=11}} | |||
Thin periodicals called [[American comic book|comic books]] appeared in the 1930s, at first reprinting newspaper comic strips; by the end of the decade, original content began to dominate.{{sfn|Rhoades|2008|p=2}} The success in 1938 of ''[[Action Comics]]'' and its lead hero [[Superman]] marked the beginning of the [[Golden Age of Comic Books]], in which the [[Superhero comics|superhero genre]] was prominent.{{sfn|Rhoades|2008|p=x}} In the UK and the [[Commonwealth of Nations|Commonwealth]], the [[DC Thomson]]-created ''[[The Dandy|Dandy]]'' (1937) and ''[[The Beano|Beano]]'' (1938) became successful humor-based titles, with a combined circulation of over 2 million copies by the 1950s. Their characters, including "[[Dennis the Menace (UK)|Dennis the Menace]]", "[[Desperate Dan]]" and "[[The Bash Street Kids]]" have been read by generations of British children.{{sfn|Childs|Storry|2013|p=532}} The comics originally experimented with superheroes and action stories before settling on humorous strips featuring a mix of the Amalgamated Press and US comic book styles.{{sfn|Bramlett|Cook|Meskin|2016|p=46}} | |||
[[File:WonderworldComics3.jpg|thumb|upright|alt=|[[Superhero comics|Superheroes]] have been a staple of [[American comic book]]s (''Wonderworld Comics'' {{No.}}3, 1939; cover: [[Flame (comics)|The Flame]] by [[Will Eisner]]).]] | |||
The popularity of superhero comic books declined in the years following World War II,{{sfn|Gabilliet|2010|p=51}} while comic book sales continued to increase as other genres proliferated, such as [[Romance comics|romance]], [[Western comics|westerns]], [[Crime comics|crime]], [[Horror comics|horror]], and humour.{{sfn|Gabilliet|2010|p=49}} Following a sales peak in the early 1950s, the content of comic books (particularly crime and horror) was subjected to scrutiny from parent groups and government agencies, which culminated in [[United States Senate Subcommittee on Juvenile Delinquency|Senate hearings]] that led to the establishment of the [[Comics Code Authority]] self-censoring body.{{sfn|Gabilliet|2010|pp=49–50}} The Code has been blamed for stunting the growth of American comics and maintaining its low status in American society for much of the remainder of the century.{{sfn|Gabilliet|2010|p=50}} Superheroes re-established themselves as the most prominent comic book genre by the early 1960s.{{sfn|Gabilliet|2010|pp=52–55}} [[Underground comix]] challenged the Code and readers with adult, countercultural content in the late 1960s and early 1970s.{{sfn|Gabilliet|2010|p=66}} The underground gave birth to the [[alternative comics]] movement in the 1980s and its mature, often experimental content in non-superhero genres.{{sfnm|1a1=Hatfield|1y=2005|1pp=20, 26|2a1=Lopes|2y=2009|2p=123|3a1=Rhoades|3y=2008|3p=140}} | |||
Comics in the US has had a [[Low culture|lowbrow]] reputation stemming from its roots in [[mass culture]]; cultural elites sometimes saw popular culture as threatening culture and society. In the latter half of the 20th century, popular culture won greater acceptance, and the lines between high and low culture began to blur. Comics nevertheless continued to be stigmatized, as the medium was seen as entertainment for children and illiterates.{{sfn|Lopes|2009|pp=xx–xxi}} | |||
The [[graphic novel]]—book-length comics—began to gain attention after [[Will Eisner]] popularized the term with his book ''[[A Contract with God]]'' (1978).{{sfn|Petersen|2010|p=222}} The term became widely known with the public after the commercial success of ''[[Maus]]'', ''[[Watchmen]]'', and ''[[The Dark Knight Returns]]'' in the mid-1980s.{{sfnm|1a1=Kaplan|1y=2008|1p=172|2a1=Sabin|2y=1993|2p=246|3a1=Stringer|3y=1996|3p=262|4a1=Ahrens|4a2=Meteling|4y=2010|4p=1|5a1=Williams|5a2=Lyons|5y=2010|5p=7}} In the 21st century graphic novels became established in mainstream bookstores{{sfn|Gabilliet|2010|pp=210–211}} and libraries{{sfn|Lopes|2009|p=151–152}} and webcomics became common.{{sfn|Thorne|2010|p=209}} | |||
===Franco-Belgian and European comics=== | |||
{{main|European comics|Franco-Belgian comics}} | |||
The francophone Swiss [[Rodolphe Töpffer]] produced comic strips beginning in 1827,{{sfn|Gabilliet|2010|p=xiv}} and published theories behind the form.{{sfn|Harvey|2010}} [[Wilhelm Busch]] first published his [[Max and Moritz]] in 1865.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.deutschland.de/en/topic/culture/arts-architecture/150-years-of-max-and-moritz | title=150 years of Max and Moritz | date=22 October 2015 }}</ref> Cartoons appeared widely in newspapers and magazines from the 19th century.{{sfn|Lefèvre|2010|p=186}} The success of ''[[Zig et Puce]]'' in 1925 popularized the use of speech balloons in European comics, after which Franco-Belgian comics began to dominate.{{sfnm|1a1=Vessels|1y=2010|1p=45|2a1=Miller|2y=2007|2p=17}} ''[[The Adventures of Tintin]]'', with its signature [[Ligne claire|clear line]] style,{{sfnm|1a1=Screech|1y=2005|1p=27|2a1=Miller|2y=2007|2p=18}} was first serialized in newspaper comics supplements beginning in 1929,{{sfn|Miller|2007|p=17}} and became an icon of Franco-Belgian comics.{{sfnm|1a1=Theobald|1y=2004|1p=82|2a1=Screech|2y=2005|2p=48|3a1=McKinney|3y=2011|3p=3}} | |||
Following the success of {{lang|fr|[[Le Journal de Mickey]]}} (est. 1934),{{sfn|Grove|2005|pp=76–78}} dedicated comics magazines{{sfnm|1a1=Petersen|1y=2010|1pp=214–215|2a1=Lefèvre|2y=2010|2p=186}} like ''[[Spirou (magazine)|Spirou]]'' (est. 1938) and ''[[Tintin (magazine)|Tintin]]'' (1946–1993), and full-colour comic albums became the primary outlet for comics in the mid-20th century.{{sfn|Petersen|2010|pp=214–215}} As in the US, at the time comics were seen as infantile and a threat to culture and literacy; commentators stated that "none bear up to the slightest serious analysis",{{efn|{{langx|fr|"... aucune ne supporte une analyse un peu serieuse."}} – Jacqueline & Raoul Dubois in {{lang|fr|La Presse enfantine française}} (Midol, 1957){{sfn|Grove|2005|p=46}} }} and that comics were "the sabotage of all art and all literature".{{sfn|Grove|2005|pp=45–46}}{{efn|{{langx|fr|"C'est le sabotage de tout art et de toute littérature."}} – Jean de Trignon in {{lang|fr|Histoires de la littérature enfantine de ma Mère l'Oye au Roi Babar}} ([[Hachette (publisher)|Hachette]], 1950){{sfn|Grove|2005|p=46}} }} | |||
In the 1960s, the term {{lang|fr|bandes dessinées}} ("drawn strips") came into wide use in French to denote the medium.{{sfn|Grove|2005|p=51}} Cartoonists began creating comics for mature audiences,{{sfnm|1a1=Miller|1y=1998|1p=116|2a1=Lefèvre|2y=2010|2p=186}} and the term "Ninth Art"{{efn|{{langx|fr|neuvième art}} }} was coined, as comics began to attract public and academic attention as an artform.{{sfn|Miller|2007|p=23}} A group including [[René Goscinny]] and [[Albert Uderzo]] founded the magazine ''[[Pilote]]'' in 1959 to give artists greater freedom over their work. Goscinny and Uderzo's ''[[Asterix|The Adventures of Asterix]]'' appeared in it{{sfn|Miller|2007|p=21}} and went on to become the best-selling French-language comics series.{{sfn|Screech|2005|p=204}} From 1960, the satirical and taboo-breaking ''[[Hara-Kiri (magazine)|Hara-Kiri]]'' defied censorship laws in the countercultural spirit that led to the [[May 1968 events in France|May 1968 events]].{{sfn|Miller|2007|p=22}} | |||
Frustration with censorship and editorial interference led to a group of ''Pilote'' cartoonists to found the adults-only ''[[L'Écho des savanes]]'' in 1972. Adult-oriented and experimental comics flourished in the 1970s, such as in the experimental science fiction of [[Jean Giraud|Mœbius]] and others in ''[[Métal hurlant]]'', even mainstream publishers took to publishing prestige-format [[adult comics]].{{sfn|Miller|2007|pp=25–28}} | |||
From the 1980s, mainstream sensibilities were reasserted and serialization became less common as the number of comics magazines decreased and many comics began to be published directly as albums.{{sfn|Miller|2007|pp=33–34}} Smaller publishers such as [[L'Association]]{{sfn|Beaty|2007|p=9}} that published longer works{{sfn|Lefèvre|2010|pp=189–190}} in non-traditional formats{{sfn|Grove|2005|p=153}} by ''[[Auteur theory|auteur]]''-istic creators also became common. Since the 1990s, mergers resulted in fewer large publishers, while smaller publishers proliferated. Sales overall continued to grow despite the trend towards a shrinking print market.{{sfn|Miller|2007|pp=49–53}} | |||
===Japanese comics=== | |||
{{main|History of manga|Manga}} | |||
[[File:Tagosaku to Mokube no Tokyo Kenbutsu.jpg|thumb|alt=|[[Rakuten Kitazawa]] created the first modern Japanese comic strip. (''Tagosaku to Mokube no Tōkyō Kenbutsu'',{{efn|{{Nihongo|''Tagosaku and Mokube Sightseeing in Tokyo''|田吾作と杢兵衛の東京見物|''Tagosaku to Mokube no Tokyo Kenbutsu''|lead=yes}} }} 1902)]] | |||
Japanese comics and cartooning (''{{transl|ja|[[manga]]}}''),{{efn|{{Nihongo|''"Manga"''|漫画||lead=yes}} can be [[gloss (annotation)|glossed]] in many ways, amongst them "whimsical pictures", "disreputable pictures",{{sfn|Karp|Kress|2011|p=19}} "irresponsible pictures",{{sfn|Gravett|2004|p=9}} "derisory pictures", and "sketches made for or out of a sudden inspiration".{{sfn|Johnson-Woods|2010|p=22}} }} have a history that has been seen as far back as the anthropomorphic characters in the 12th-to-13th-century ''{{transl|ja|[[Chōjū-jinbutsu-giga]]}}'', 17th-century ''{{transl|ja|[[toba-e]]}}'' and ''{{transl|ja|[[kibyōshi]]}}'' picture books,{{sfn|Schodt|1996|p=22}} and [[Woodblock printing|woodblock prints]] such as [[ukiyo-e]] which were popular between the 17th and 20th centuries. The ''{{transl|ja|kibyōshi}}'' contained examples of sequential images, movement lines,{{sfn|Mansfield|2009|p=253}} and sound effects.{{sfn|Petersen|2010|p=42}} | |||
Illustrated magazines for Western expatriates introduced Western-style satirical cartoons to Japan in the late 19th century. New publications in both the Western and Japanese styles became popular, and at the end of the 1890s, American-style newspaper comics supplements began to appear in Japan,{{sfn|Johnson-Woods|2010|pp=21–22}} as well as some American comic strips.{{sfn|Schodt|1996|p=22}} 1900 saw the debut of the ''Jiji Manga'' in the ''Jiji Shinpō'' newspaper—the first use of the word "manga" in its modern sense,{{sfn|Johnson-Woods|2010|p=22}} and where, in 1902, [[Rakuten Kitazawa]] began the first modern Japanese comic strip.{{sfnm|1a1=Petersen|1y=2010|1p=128|2a1=Gravett|2y=2004|2p=21}} By the 1930s, comic strips were serialized in large-circulation monthly girls' and boys' magazine and collected into hardback volumes.{{sfnm|1a1=Schodt|1y=1996|1p=22|2a1=Johnson-Woods|2y=2010|2pp=23–24}} | |||
The modern era of comics in Japan began after World War II, propelled by the success of the serialized comics of the prolific [[Osamu Tezuka]]{{sfn|Gravett|2004|p=24}} and the comic strip ''[[Sazae-san]]''.{{sfnm|1a1=MacWilliams|1y=2008|1p=3|2a1=Hashimoto|2a2=Traphagan|2y=2008|2p=21|3a1=Sugimoto|3y=2010|3p=255|4a1=Gravett|4y=2004|4p=8}} Genres and audiences diversified over the following decades. Stories are usually first serialized in magazines which are often hundreds of pages thick and may contain over a dozen stories;{{sfnm|1a1=Schodt|1y=1996|1p=23|2a1=Gravett|2y=2004|2pp=13–14}} they are later compiled in {{transl|ja|[[tankōbon]]}}-format books.{{sfn|Gravett|2004|p=14}} At the turn of the 20th and 21st centuries, nearly a quarter of all printed material in Japan was comics.{{sfnm|1a1=Brenner|1y=2007|1p=13|2a1=Lopes|2y=2009|2p=152|3a1=Raz|3y=1999|3p=162|4a1=Jenkins|4y=2004|4p=121}} Translations became extremely popular in foreign markets—in some cases equaling or surpassing the sales of domestic comics.{{sfn|Lee|2010|p=158}} | |||
==Forms and formats== | |||
[[Comic strip]]s are generally short, multipanel comics that have, since the early 20th century, most commonly appeared in newspapers. In the US, daily strips have normally occupied a single tier, while [[Sunday comics|Sunday strips]] have been given multiple tiers. Since the early 20th century, daily newspaper comic strips have typically been printed in black-and-white and Sunday comics have usually been printed in colour and have often occupied a full newspaper page.{{sfn|Booker|2014|p=xxvi–xxvii}} | |||
Specialized comics periodicals formats vary greatly in different cultures. [[Comic book]]s, primarily an American format, are thin periodicals{{sfnm|1a1=Orr|1y=2008|1p=11|2a1=Collins|2y=2010|2p=227}} usually published in colour.{{sfn|Orr|2008|p=10}} European and Japanese comics are frequently serialized in magazines—monthly or weekly in Europe,{{sfn|Johnson-Woods|2010|p=22}} and usually black-and-white and weekly in Japan.{{sfnm|1a1=Schodt|1y=1996|1p=23|2a1=Orr|2y=2008|2p=10}} Japanese comics magazine typically run to hundreds of pages.{{sfn|Schodt|1996|p=23}} | |||
{{wide image | |||
|1 = Comics volumes - international comparison.jpg | |||
|2 = 600px | |||
|3 = A comparison of book formats for comics around the world. The left group is from Japan and shows the {{transl|ja|[[tankōbon]]}} and the smaller {{transl|ja|[[bunkobon]]}} formats. Those in the middle group of [[Franco-Belgian comics]] are in the standard [[ISO 216#A4 series|A4-size]] [[comic album]] format. The right group of [[graphic novel]]s is from English-speaking countries, where there is no standard format.}} | |||
Book-length comics take different forms in different cultures. European [[comic albums]] are most commonly colour volumes printed at [[ISO 216#A4 series|A4-size]], a larger page size than used in many other cultures.{{sfnm|1a1=Grove|1y=2010|1p=24|2a1=McKinney|2y=2011|p={{not a typo|xiii}}}}{{sfn|Petersen|2010|pp=214–215}} In English-speaking countries, the [[trade paperback (comics)|trade paperback]] format originating from collected comic books have also been chosen for original material. Otherwise, bound volumes of comics are called graphic novels and are available in various formats. Despite incorporating the term "novel"—a term normally associated with fiction—"graphic novel" also refers to non-fiction and collections of short works.{{sfnm|1a1=Goldsmith|1y=2005|1p=16|2a1=Karp|2a2=Kress|2y=2011|2pp=4–6}} Japanese comics are collected in volumes called {{Lang|ja-latn|[[tankōbon]]}} following magazine serialization.{{sfn|Poitras|2001|p=66–67}} | |||
[[Gag cartoon|Gag]] and [[editorial cartoon]]s usually consist of a single panel, often incorporating a caption or speech balloon. Definitions of comics which emphasize sequence usually exclude gag, editorial, and other single-panel cartoons; they can be included in definitions that emphasize the combination of word and image.{{sfn|Harvey|2001|p=76}} Gag cartoons first began to proliferate in [[broadsheet]]s published in Europe in the 18th and 19th centuries, and the term "cartoon"{{efn|"[[wikt:cartoon|cartoon]]": from the Italian {{lang|it|cartone}}, meaning "card", which referred to the cardboard on which the cartoons were typically drawn.{{sfn|Harvey|2001|p=77}} }} was first used to describe them in 1843 in the British humour magazine ''[[Punch (magazine)|Punch]]''.{{sfn|Harvey|2001|p=77}} | |||
[[Webcomic]]s are comics that are available on the internet, first being published the 1980s. They are able to potentially reach large audiences, and new readers can often access archives of previous installments.{{sfn|Petersen|2010|pp=234–236}} Webcomics can make use of an [[infinite canvas]], meaning they are not constrained by the size or dimensions of a printed comics page.{{sfnm|1a1=Petersen|1y=2010|1p=234|2a1=McCloud|2y=2000|2p=222}} | |||
Some consider [[storyboard]]s{{sfn|Rhoades|2008|p=38}} and [[wordless novel]]s to be comics.{{sfn|Beronä|2008|p=225}} Film studios, especially in animation, often use sequences of images as guides for film sequences. These storyboards are not intended as an end product and are rarely seen by the public.{{sfn|Rhoades|2008|p=38}} Wordless novels are books which use sequences of captionless images to deliver a narrative.{{sfn|Cohen|1977|p=181}} | |||
==Comics studies== | |||
{{Main|Comics studies}} | |||
<!-- ''Note: Although it takes the form of a plural noun, the common usage when referring to ''comics'' as a medium is to treat it as singular.'' --> | |||
{{quote box|"Comics ... are sometimes four-legged and sometimes two-legged and sometimes fly and sometimes don't ... to employ a metaphor as mixed as the medium itself, defining comics entails cutting a Gordian-knotted enigma wrapped in a mystery ..."|source=[[R. C. Harvey]], 2001{{sfn|Harvey|2001|p=76}}|width=30em}} | |||
Similar to the problems of defining literature and film,{{sfn|Groensteen|2012|pp=128—129}} no consensus has been reached on a definition of the comics medium,{{sfn|Groensteen|2012|p=124}} and attempted definitions and descriptions have fallen prey to numerous exceptions.{{sfn|Groensteen|2012|p=126}} Theorists such as Töpffer,{{sfn|Thomas|2010|p=158}} [[R. C. Harvey]], [[Will Eisner]],{{sfn|Beaty|2012|p=65}} David Carrier,{{sfn|Groensteen|2012|pp=126, 131}} Alain Rey,{{sfn|Groensteen|2012|p=124}} and Lawrence Grove emphasize the combination of text and images,{{sfn|Grove|2010|pp=17–19}} though there are prominent examples of pantomime comics throughout its history.{{sfn|Groensteen|2012|p=126}} Other critics, such as Thierry Groensteen{{sfn|Grove|2010|pp=17–19}} and Scott McCloud, have emphasized the primacy of sequences of images.{{sfn|Thomas|2010|pp=157, 170}} Towards the close of the 20th century, different cultures' discoveries of each other's comics traditions, the rediscovery of forgotten early comics forms, and the rise of new forms made defining comics a more complicated task.{{sfn|Groensteen|2012a|pp=112–113}} | |||
European comics studies began with Töpffer's theories of his own work in the 1840s, which emphasized panel transitions and the visual–verbal combination. No further progress was made until the 1970s.{{sfn|Miller|2007|p=101}} Pierre Fresnault-Deruelle then took a [[semiotics]] approach to the study of comics, analyzing text–image relations, page-level image relations, and image discontinuities, or what Scott McCloud later dubbed "closure".{{sfn|Groensteen|2012a|p=112}} In 1987, Henri Vanlier introduced the term {{lang|fr|multicadre}}, or "multiframe", to refer to the comics page as a semantic unit.{{sfn|Groensteen|2012a|p=113}} By the 1990s, theorists such as [[Benoît Peeters]] and [[Thierry Groensteen]] turned attention to artists' [[Poiesis|poïetic]] creative choices.{{sfn|Groensteen|2012a|p=112}} [[Thierry Smolderen]] and Harry Morgan have held relativistic views of the definition of comics, a medium that has taken various, equally valid forms over its history. Morgan sees comics as a subset of "{{lang|fr|les littératures dessinées}}" (or "drawn literatures").{{sfn|Groensteen|2012a|pp=112–113}} French theory has come to give special attention to the page, in distinction from American theories such as McCloud's which focus on panel-to-panel transitions.{{sfn|Groensteen|2012a|p=113}} In the mid-2000s, [[Neil Cohn]] began analyzing how comics are understood using tools from cognitive science, extending beyond theory by using actual psychological and neuroscience experiments. This work has argued that sequential images and page layouts both use separate rule-bound "grammars" to be understood that extend beyond panel-to-panel transitions and categorical distinctions of types of layouts, and that the brain's comprehension of comics is similar to comprehending other domains, such as language and music.{{sfn|Cohn|2013}} | |||
Historical narratives of ''manga'' tend to focus either on its recent, post-WWII history, or on attempts to demonstrate deep roots in the past, such as to the ''{{transl|ja|Chōjū-jinbutsu-giga}}'' picture scroll of the 12th and 13th centuries, or the early 19th-century ''Hokusai Manga''.{{sfn|Stewart|2014|pp=28–29}} The first historical overview of Japanese comics was Seiki Hosokibara's {{transl|ja|Nihon Manga-Shi}}{{efn|{{cite book|last=Hosokibara|first=Seiki|trans-title=Japanese Comics History|title=日本漫画史|publisher=Yuzankaku|year=1924}} }} in 1924.{{sfnm|1a1=Johnson-Woods|1y=2010|1p=23|2a1=Stewart|2y=2014|2p=29}} Early post-war Japanese criticism was mostly of a left-wing political nature until the 1986 publication of Tomofusa Kure's ''Modern Manga: The Complete Picture'',{{efn|{{cite book|first=Tomofusa|last=Kure|trans-title=Modern Manga: The Complete Picture|title=現代漫画の全体像|publisher=Joho Center Publishing|year=1986|isbn=978-4-575-71090-8}}{{sfn|Kinsella|2000|pp=96–97}} }} which de-emphasized politics in favour of formal aspects, such as structure and a "grammar" of comics. The field of {{transl|ja|manga}} studies increased rapidly, with numerous books on the subject appearing in the 1990s.{{sfn|Kinsella|2000|pp=96–97}} Formal theories of ''{{transl|ja|manga}}'' have focused on developing a "manga expression theory",{{efn|{{Nihongo|"Manga expression theory"|漫画表現論|manga hyōgenron|lead=yes}}{{sfn|Kinsella|2000|p=100}} }} with emphasis on spatial relationships in the structure of images on the page, distinguishing the medium from film or literature, in which the flow of time is the basic organizing element.{{sfn|Kinsella|2000|p=100}} Comics studies courses have proliferated at Japanese universities, and Japan Society for Studies in Cartoon and Comics {{small|([[:ja:日本マンガ学会|ja]])}}{{efn|{{Nihongo|Japan Society for Studies in Cartoon and Comics|日本マンガ学会|Nihon Manga Gakkai|lead=yes}} }} was established in 2001 to promote comics scholarship.{{sfn|Morita|2010|pp=37–38}} The publication of [[Frederik L. Schodt]]'s ''[[Manga! Manga! The World of Japanese Comics]]'' in 1983 led to the spread of use of the word ''manga'' outside Japan to mean "Japanese comics" or "Japanese-style comics".{{sfn|Stewart|2014|p=30}} | |||
{{Multiple image | |||
| align = right | |||
| total_width = 300 | |||
| direction = | |||
| image1 = Will Eisner (San Diego Comic Con, 2004).jpg | |||
| alt1 = An elderly bald man wearing glasses. | |||
| image2 = Scott McCloud.Making Comics Tour.RISD.gk.JPG | |||
| alt2 = A middle-aged man seated behind a table, facing the camera. | |||
| footer = [[Will Eisner]] ''(left)'' and [[Scott McCloud]] (right) have proposed influential and controversial definitions of comics. | |||
}} | |||
[[Coulton Waugh]] attempted the first comprehensive history of American comics with ''The Comics'' (1947).{{sfn|Inge|1989|p=214}} Will Eisner's ''[[Comics and Sequential Art]]'' (1985) and [[Scott McCloud]]'s ''[[Understanding Comics]]'' (1993) were early attempts in English to formalize the study of comics. David Carrier's ''The Aesthetics of Comics'' (2000) was the first full-length treatment of comics from a philosophical perspective.{{sfn|Meskin|Cook|2012|p=xxix}} Prominent American attempts at definitions of comics include Eisner's, McCloud's, and Harvey's. Eisner described what he called "[[sequential art]]" as "the arrangement of pictures or images and words to narrate a story or dramatize an idea";{{sfnm|1a1=Yuan|1y=2011|2a1=Eisner|2y=1985|2p=5}} Scott McCloud defined comics as "juxtaposed pictorial and other images in deliberate sequence, intended to convey information and/or to produce an aesthetic response in the viewer",{{sfnm|1a1=Kovacs|1a2=Marshall|1y=2011|1p=10|2a1=Holbo|2y=2012|2p=13|3a1=Harvey|3y=2010|3p=1|4a1=Beaty|4y=2012|4p=6|5a1=McCloud|5y=1993|5p=9}} a strictly formal definition which detached comics from its historical and cultural trappings.{{sfn|Beaty|2012|p=67}} R. C. Harvey defined comics as "pictorial narratives or expositions in which words (often lettered into the picture area within speech balloons) usually contribute to the meaning of the pictures and vice versa".{{sfnm|1a1=Chute|1y=2010|1p=7|2a1=Harvey|2y=2001|2p=76}} Each definition has had its detractors. Harvey saw McCloud's definition as excluding single-panel cartoons,{{sfn|Harvey|2010|p=1}} and objected to McCloud's de-emphasizing verbal elements, insisting "the essential characteristic of comics is the incorporation of verbal content".{{sfn|Groensteen|2012a|p=113}} Aaron Meskin saw McCloud's theories as an artificial attempt to legitimize the place of comics in art history.{{sfn|Beaty|2012|p=65}} | |||
Cross-cultural study of comics is complicated by the great difference in meaning and scope of the words for "comics" in different languages.{{sfn|Morita|2010|p=33}} The French term for comics, {{lang|fr|bandes dessinées}} ("drawn strip") emphasizes the juxtaposition of drawn images as a defining factor,{{sfnm|1a1=Groensteen|1y=2012|1p=130|2a1=Morita|2y=2010|2p=33}} which can imply the exclusion of even photographic comics.{{sfn|Groensteen|2012|p=130}} The term ''{{transl|ja|manga}}'' is used in Japanese to indicate all forms of comics, cartooning,{{sfn|Johnson-Woods|2010|p=336}} and caricature.{{sfn|Morita|2010|p=33}} | |||
==Terminology== | |||
{{Main|Glossary of comics terminology}} | |||
The term ''comics'' refers to the comics medium when used as an [[uncountable noun]] and thus takes the singular: "comics ''is'' a medium" rather than "comics ''are'' a medium". When ''comic'' appears as a countable noun it refers to instances of the medium, such as individual comic strips or comic books: "Tom's comics ''are'' in the basement."{{sfnm|1a1=Chapman|1y=2012|1p=8|2a1=Chute|2a2=DeKoven|2y=2012|2p=175|3a1=Fingeroth|3y=2008|3p=4}} | |||
Panels are individual images containing a segment of action,{{sfn|Lee|1978|p=15}} often surrounded by a border.{{sfn|Eisner|1985|pp=28, 45}} Prime moments in a narrative are broken down into panels via a process called encapsulation.{{sfn|Duncan|Smith|2009|p=10}} The reader puts the pieces together via the process of closure by using background knowledge and an understanding of panel relations to combine panels mentally into events.{{sfn|Duncan|Smith|2009|p=316}} The size, shape, and arrangement of panels each affect the timing and pacing of the narrative.{{sfn|Eisner|1985|p=30}} The contents of a panel may be asynchronous, with events depicted in the same image not necessarily occurring at the same time.{{sfnm|1a1=Duncan|1a2=Smith|1y=2009|1p=315|2a1=Karp|2a2=Kress|2y=2011|2p=12–13}} | |||
[[File:PunchandJudyComicsV01-0145-panel3.jpg|thumb|alt=A comics panel. In the top left, a caption with a yellow background reads, "Suddenly the street is filled with angry people!" In the main panel, anthropomorphic characters crowd a sidewalk. A monkey, standing to the left on the road beside the curb, says, "Gosh! Where'd all these people come from?" An overweight male on the sidewalk in the middle facing right says to a police officer, "Hey! My watch disappeared from my parlor!" A female near the bottom right, says to a male in the bottom right corner, "My necklace! It's gone from the table!!"|A caption (the yellow box) gives the narrator a voice. The characters' dialogue appears in [[speech balloon]]s. The tail of the balloon indicates the speaker.]] | |||
Text is frequently incorporated into comics via [[speech balloon]]s, captions, and sound effects. Speech balloons indicate dialogue (or thought, in the case of [[thought balloon]]s), with tails pointing at their respective speakers.{{sfnm|1a1=Lee|1y=1978|1p=15|2a1=Markstein|2y=2010|3a1=Eisner|3y=1985|3p=157|4a1=Dawson|4y=2010|4p=112|5a1=Saraceni|5y=2003|5p=9}} Captions can give voice to a narrator, convey characters' dialogue or thoughts,{{sfnm|1a1=Lee|1y=1978|1p=15|2a1=Lyga|2a2=Lyga|2y=2004|p=161}} or indicate place or time.{{sfnm|1a1=Saraceni|1y=2003|1p=9|2a1=Karp|2a2=Kress|2y=2011|2p=18}} Speech balloons themselves are strongly associated with comics, such that the addition of one to an image is sufficient to turn the image into comics.{{sfn|Forceville|Veale|Feyaerts|2010|p=56}} Sound effects mimic non-vocal sounds textually using [[onomatopoeia]] sound-words.{{sfn|Duncan|Smith|2009|pp=156, 318}} | |||
[[Cartooning]] is most frequently used in making comics, traditionally using ink (especially [[India ink]]) with [[dip pen]]s or ink brushes;{{sfnm|1a1=Markstein|1y=2010|2a1=Lyga|2a2=Lyga|2y=2004|2p=161|3a1=Lee|3y=1978|3p=145|4a1=Rhoades|4y=2008|4p=139}} mixed media and digital technology have become common. Cartooning techniques such as [[motion lines]]{{sfnm|1a1=Bramlett|1y=2012|1p=25|2a1=Guigar|2y=2010|2p=126|3a1=Cates|3y=2010|3p=98}} and abstract symbols are often employed.{{sfnm|1a1=Goldsmith|1y=2005|1p=21|2a1=Karp|2a2=Kress|2y=2011|2p=13–14}} | |||
While comics are often the work of a single creator, the labour of making them is frequently divided between a number of specialists. There may be separate [[Comics writer|writers]] and [[Comics artist|artists]], and artists may specialize in parts of the artwork such as characters or backgrounds, as is common in Japan.{{sfn|O'Nale|2010|p=384}} Particularly in American superhero comic books,{{sfn|Tondro|2011|p=51}} the art may be divided between a [[penciller]], who lays out the artwork in pencil;{{sfn|Lyga|Lyga|2004|p=161}} an [[inker]], who finishes the artwork in ink;{{sfnm|1a1=Markstein|1y=2010|2a1=Lyga|2a2=Lyga|2y=2004|2p=161|3a1=Lee|3y=1978|3p=145}} a [[Colorist|colourist]];{{sfn|Duncan|Smith|2009|p=315}} and a [[letterer]], who adds the captions and speech balloons.{{sfn|Lyga|Lyga|2004|p=163}} | |||
===Etymology=== | |||
The English-language term ''comics'' derives from the humorous (or "[[wikt:comic|comic]]") work which predominated in early American newspaper comic strips, but usage of the term has become standard for non-humorous works as well. The alternate spelling ''comix'' – coined by the [[underground comix]] movement – is sometimes used to address such ambiguities.{{sfn|Gomez Romero|Dahlman|2012}} The term "comic book" has a similarly confusing history since they are most often not humorous and are periodicals, not regular books.{{sfn|Groensteen|2012|loc=p. 131 (translator's note)}} It is common in English to refer to the comics of different cultures by the terms used in their languages, such as ''{{transl|ja|[[manga]]}}'' for Japanese comics, or {{lang|fr|bandes dessinées}} for French-language [[Franco-Belgian comics]].{{sfn|McKinney|2011|p=xiii}} | |||
Many cultures have taken their word for comics from English, including Russian ({{lang|ru|комикс}}, ''{{transl|ru|[[Russian comics|komiks]]}}''){{sfn|Alaniz|2010|p=7}} and German ({{lang|de|[[German comics|Comic]]}}).{{sfn|Frahm|2003}} Similarly, the Chinese term ''{{transl|zh|[[manhua]]}}''{{sfnm|1a1=Wong|1y=2002|1p=11|2a1=Cooper-Chen|2y=2010|2p=177}} and the Korean ''{{transl|ko|[[manhwa]]}}''{{sfn|Johnson-Woods|2010|p=301}} derive from the [[Chinese character]]s with which the Japanese term ''{{transl|ja|manga}}'' is written.{{sfnm|1a1=Cooper-Chen|1y=2010|1p=177|2a1=Thompson|2y=2007|2p=xiii}} | |||
==See also== | |||
{{Div col|colwidth=20em}} | |||
* [[Animation]] | |||
* [[Billy Ireland Cartoon Library & Museum]] | |||
* [[Picture book]] | |||
{{Div col end}} | |||
===See also lists=== | |||
{{Div col|colwidth=20em}} | |||
* [[List of best-selling comic series]] | |||
* [[List of best-selling manga]] | |||
* [[List of comic books]] | |||
* [[List of comics by country]] | |||
* [[List of comics creators]] | |||
* [[List of comics publishing companies]] | |||
* [[List of comic strip syndicates]] | |||
* [[List of Franco-Belgian comics series]] | |||
* [[List of newspaper comic strips]] | |||
* [[Lists of manga]] | |||
* [[List of manga artists]] | |||
* [[List of manga magazines]] | |||
* [[List of manga publishers]] | |||
* [[List of years in comics]] | |||
{{Div col end}} | |||
==Notes== | |||
{{Notelist}} | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|24em}} | |||
===Works cited=== | |||
====Books==== | |||
{{Refbegin|30em}} | |||
* {{cite book |last1=Ahrens |first1=Jörn |last2=Meteling |first2=Arno |title=Comics and the City: Urban Space in Print, Picture, and Sequence |publisher=[[Continuum International Publishing Group]] |year=2010 |isbn=978-0-8264-4019-8}}<!-- Ahrens Mateling 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Alaniz |first=José |title=Komiks: Comic Art in Russia |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=t9oq_c5M_gQC |year=2010 |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |isbn=978-1-60473-366-2}}<!-- Alaniz 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Barker |first=Martin |title=Comics: Ideology, Power, and the Critics |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0DG8AAAAIAAJ |year=1989 |publisher=Manchester University Press |isbn=978-0-7190-2589-1}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Beaty |first=Bart |title=Unpopular Culture: Transforming the European Comic Book in The 1990s |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PXgwiPyLEpkC |year=2007 |publisher=[[University of Toronto Press]] |isbn=978-0-8020-9412-4}}<!-- Beaty 2007 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Beaty |first=Bart |title=Comics Versus Art |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xuotcKAeM5YC |year=2012 |publisher=[[University of Toronto Press]] |isbn=978-1-4426-9627-3}}<!-- Beaty 2012 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Beronä |first=David A. |title=Wordless Books: The Original Graphic Novels |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YVh2QgAACAAJ |year=2008 |publisher=[[Abrams Books]] |isbn=978-0-8109-9469-0}}<!-- Beronä 2008 --> | |||
* {{cite book |editor-last=Booker |editor-first=M. Keith |title=Comics through Time: A History of Icons, Idols, and Ideas |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hnuQBQAAQBAJ |year=2014 |publisher=[[ABC-CLIO]] |isbn=978-0-313-39751-6 |pages=xxv–xxxvii |chapter=Introduction}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Bramlett |first=Frank |title=Linguistics and the Study of Comics |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=l6MvTeifzWEC |year=2012 |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |isbn=978-0-230-36282-6}}<!-- Bramlett 2012 --> | |||
* {{cite book |title=The Routledge Companion to Comics |editor1-first=Frank |editor1-last=Bramlett |editor2-first=Roy |editor2-last=Cook |editor3-first=Aaron |editor3-last=Meskin |pages=45–6 |publisher=Routledge |year=2016 |isbn=978-1-317-91538-6}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Brenner |first=Robin E. |title=Understanding Manga and Anime |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uY8700WJy_gC |year=2007 |publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group |isbn=978-0-313-09448-4}}<!-- Brenner --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Cates |first=Isaac |chapter=Comic and the Grammar of Diagrams |pages=90–105 |title=The Comics of Chris Ware: Drawing Is a Way of Thinking |editor1-last=Ball |editor1-first=David M. |editor2-last=Kuhlman |editor2-first=Martha B. |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QrFmPKlv61sC&pg=PA90 |year=2010 |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |isbn=978-1-60473-442-3}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Chapman |first=Robyn |title=Drawing Comics Lab: 52 Exercises on Characters, Panels, Storytelling, Publishing & Professional Practices |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6kEJeAbskloC |year=2012 |publisher=Quarry Books |isbn=978-1-61058-629-0}} | |||
* {{cite book |title=Encyclopedia of Contemporary British Culture |first1=Peter |last1=Childs |first2=Michael |last2=Storry |page=532 |publisher=Routledge |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-134-75555-4}}<!-- Childs, Storry 2013 --> | |||
* {{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1Xc6QdyrQLAC |last=Chute |first=Hillary L |title=Graphic Women: Life Narrative and Contemporary Comics |publisher=[[Columbia University Press]] |year=2010 |isbn=978-0-231-15062-0}}<!-- Chute 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last1=Chute |first1=Hillary |last2=DeKoven |first2=Marianne |title=The Cambridge Companion to Popular Fiction |editor1-last=Glover |editor1-first=David |editor2-last=McCracken |editor2-first=Scott |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RBOgyekqWLwC&pg=PA175 |year=2012 |publisher=[[Cambridge University Press]] |isbn=978-0-521-51337-1 |pages=175–195 |chapter=Comic books and graphic novels}} | |||
* {{cite book |last1=Clark |first1=Alan |last2=Clark |first2=Laurel |title=Comics: An Illustrated History |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7pMiOdqPECQC |year=1991 |publisher=Green Wood |isbn=978-1-872532-55-4}}<!-- Clark & Clark 1991 --> | |||
* {{Cite book |isbn=978-1-4411-8145-9 |title=The Visual Language of Comics: Introduction to the Structure and Cognition of Sequential Images |last1=Cohn |first1=Neil |year=2013 |publisher=Bloomsbury |location=London |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RVABAQAAQBAJ&q=the+visual+language+of+comics}}<!-- Cohn 2013 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Collins |first=Rachel |chapter=Drawing Comics into Canadian Libraries |title=Graphic Novels and Comics in Libraries and Archives |editor-last=Weiner |editor-first=Robert G. |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Xo-QYdfL9DoC&pg=PA226 |year=2010 |publisher=[[McFarland & Company]] |isbn=978-0-7864-5693-2 |pages=226–241}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Cooper-Chen |first=Anne M. |title=Cartoon Cultures: The Globalization of Japanese Popular Media |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=duL8WZh9xjQC&pg=PA177 |year=2010 |publisher=[[Peter Lang (publisher)|Peter Lang]] |isbn=978-1-4331-0368-1}}<!-- Cooper-Chen 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Crespi |first=John |year=2020 |title=Manhua Modernity: Chinese Culture and the Pictorial Turn |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-97386-2}}<!-- Crespi 2020 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Dawson |first=Willow |title=Lila & Ecco's Do-It-Yourself Comics Club |url=https://archive.org/details/lilaeccosdoityou0000daws |url-access=registration |publisher=Kids Can Press Ltd |year=2010 |isbn=978-1-55453-438-8}}<!-- Dawson 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last1=Duncan |first1=Randy |last2=Smith |first2=Matthew J |year=2009 |title=The Power of Comics |publisher=Continuum International Publishing Group |isbn=978-0-8264-2936-0}}<!-- Duncan Smith 2009 --> | |||
* {{cite book |author-link=Will Eisner |first=Will |last=Eisner |title=Comics and Sequential Art |publisher=Poorhouse Press |year=1985 |isbn=978-0-9614728-0-1}}<!-- Eisner 1985 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Fingeroth |first=Danny |title=The Rough Guide to Graphic Novels |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=naIjAQAAIAAJ |year=2008 |publisher=Rough Guides |isbn=978-1-84353-993-3}} | |||
* {{cite book |first1=Charles |last1=Forceville |first2=Tony |last2=Veale |first3=Kurt |last3=Feyaerts |chapter=Balloonics: The Visuals of Balloons in Comics |page=54 |editor1-last=Goggin |editor1-first=Joyce |editor2-last=Hassler-Forest |editor2-first=Dan |title=The Rise and Reason of Comics and Graphic Literature: Critical Essays on the Form |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8yXWG0efa_8C |year=2010 |publisher=[[McFarland & Company]] |isbn=978-0-7864-4294-2}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Gabilliet |first=Jean-Paul |others=translated from French by Bart Beaty and Nick Nguyen |title=Of Comics and Men: A Cultural History of American Comic Books |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=J1t8g_yX1wcC |year=2010 |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |isbn=978-1-60473-267-2}}<!-- Gabilliet 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Goldsmith |first=Francisca |title=Graphic Novels Now: Building, Managing, And Marketing a Dynamic Collection |url=https://archive.org/details/graphicnovelsnow00fran |url-access=registration |year=2005 |publisher=[[American Library Association]] |isbn=978-0-8389-0904-1}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Gordon |first=Ian |title=Comic Strips and Consumer Culture |year=2002 |publisher=Smithsonian |isbn=978-1-58834-031-3}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Gravett |first=Paul |title=Manga: 60 Years of Japanese Comics |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VgdjrS-lYwQC |year=2004 |publisher=Laurence King Publishing |isbn=978-1-85669-391-2}}<!-- Gravett 2004 --> | |||
* {{cite book |first=Thierry |last=Groensteen |chapter=The Impossible Definition |orig-year=Originally published in French in 1999 |others=translated by Bart Beaty |pages=124–131 |editor1-last=Heer |editor1-first=Jeet |editor2-last=Worcester |editor2-first=Kent |title=A Comics Studies Reader |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EjzAZtoxfx8C |year=2012 |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |isbn=978-1-60473-109-5}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Groensteen |first=Thierry |chapter=Definitions |editor1-last=Miller |editor1-first=Ann |editor1-link=Ann Miller (comics scholar) |editor2-last=Beaty |editor2-first=Bart |title=The French Comics Theory Reader |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=F9yFBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA93 |year=2014 |publisher=[[Leuven University Press]] |isbn=978-90-5867-988-8 |pages=93–114}} | |||
* {{cite book |first=Laurence |last=Grove |title=Text/Image Mosaics in French Culture: Emblems and Comic Strips |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zQWmlJPHyeoC |year=2005 |publisher=Ashgate Publishing |isbn=978-0-7546-3488-1}}<!-- Grove 2005 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Grove |first=Laurence |title=Comics in French: The European Bande Dessinée in Context |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=B0AzqTDBdHYC |year=2010 |publisher=Berghahn Books |isbn=978-1-84545-588-0}}<!-- Grove 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Guigar |first=Brad J. |title=The Everything Cartooning Book: Create Unique And Inspired Cartoons For Fun And Profit |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Up2EIiw4z0cC |year=2010 |publisher=Adams Media |isbn=978-1-4405-2306-9}}<!-- Guigar 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |author-link=R. C. Harvey |last=Harvey |first=R. C. |year=1994 |title=The Art of the Funnies: An Aesthetic History |url=https://archive.org/details/artoffunniesaest0000harv |url-access=registration |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |isbn=978-0-87805-674-3}}<!-- Harvey 1994 --> | |||
* {{cite book |first=R. C. |last=Harvey |author-link=R. C. Harvey |chapter=Comedy at the Juncture of Word and Image |pages=75–96 |editor1-last=Varnum |editor1-first=Robin |editor2-last=Gibbons |editor2-first=Christina T. |title=The Language of Comics: Word and Image |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |year=2001 |isbn=978-1-57806-414-4}} | |||
* {{cite book |last1=Hashimoto |first1=Akiko |last2=Traphagan |first2=John W. |title=Imagined Families, Lived Families: Culture and Kinship in Contemporary Japan |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fZO-VDjti9MC |year=2008 |publisher=[[SUNY Press]] |isbn=978-0-7914-7577-5}}<!-- Hashimoto Traphagan 2008 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Hatfield |first=Charles |title=Alternative Comics: An Emerging Literature |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mWfi_GHJV0MC |year=2005 |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |isbn=978-1-57806-719-0}}<!-- Hatfield 2005 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Holbo |first=John |chapter=Redefining Comics |title=The Art of Comics: A Philosophical Approach |editor1-last=Meskin |editor1-first=Aaron |editor2-last=Cook |editor2-first=Roy T. |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KLzSI5V5-h8C&pg=PA13 |year=2012 |publisher=[[John Wiley & Sons]] |isbn=978-1-4443-3464-7 |pages=3–30}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Inge |first=Thomas M. |title=Handbook of American Popular Culture |url=https://archive.org/details/handbookofameric01inge |url-access=registration |year=1989 |publisher=Greenwood Press |isbn=978-0-313-25406-2}}<!-- Inge 1989 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Jenkins |first=Henry |chapter=Pop Cosmopolitanism: Mapping Cultural Flows in an Age of Media Convergence |pages=114–140 |editor1-last=Suárez-Orozco |editor1-first=Marcelo M. |editor2-last=Qin-Hilliard |editor2-first=Desirée Baolian |title=Globalization: Culture and Education for a New Millennium |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rc7FRbkkzsEC |year=2004 |publisher=[[University of California Press]] |isbn=978-0-520-24125-1}} | |||
* {{cite book |editor1-last=Wannamaker |editor1-first=Annette |editor2-last=Abate |editor2-first=Michelle Ann |last=Jobs |first=Richard Ivan |title=Global Perspectives on Tarzan: From King of the Jungle to International Icon |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=B5wP-g-Arx4C&pg=PA73 |year=2012 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-136-44791-4 |pages=73–106 |chapter=Tarzan under Attack}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Johnson-Woods |first=Toni |title=Manga: An Anthology of Global and Cultural Perspectives |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ThfHNyM3f-4C |year=2010 |publisher=Continuum International Publishing Group |isbn=978-0-8264-2938-4}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Kaplan |first=Arie |title=From Krakow to Krypton: Jews and Comic Books |publisher=[[Jewish Publication Society]] |year=2008 |isbn=978-0-8276-0843-6}} | |||
* {{cite book |last1=Karp |first1=Jesse |last2=Kress |first2=Rush |title=Graphic Novels in Your School Library |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AizO7StJA1kC |year=2011 |publisher=[[American Library Association]] |isbn=978-0-8389-1089-4}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Kinsella |first=Sharon |title=Adult Manga: Culture & Power in Contemporary Japanese Society |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OudYqWuAlSwC |year=2000 |publisher=[[University of Hawaii Press]] |isbn=978-0-8248-2318-4}} | |||
* {{cite book |last1=Kovacs |first1=George |last2=Marshall |first2=C.W. |title=Classics and Comics |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fyUJoZ8oPVEC |year=2011 |publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |isbn=978-0-19-979290-0}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Lee |first=Hye-Kyung |chapter=Between Fan Culture and Copyright Infringement: Manga Scanlation |title=Marketing the Arts: A Fresh Approach |editor1-last=O'Reilly |editor1-first=Daragh |editor2-last=Kerrigan |editor2-first=Finola |pages=153–170 |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QXCUKvif0TQC |year=2010 |publisher=[[Taylor & Francis]] |isbn=978-0-415-49685-8}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Lee |first=Stan |author-link=Stan Lee |title=How to Draw Comics the Marvel Way |publisher=[[Simon & Schuster]] |year=1978 |isbn=978-0-671-53077-8 |title-link=How to Draw Comics the Marvel Way}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Lopes |first=Paul |title=Demanding Respect: The Evolution of the American Comic Book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yYInVE6OLiQC |year=2009 |publisher=Temple University Press |isbn=978-1-59213-443-4}} | |||
* {{cite book |first=Pascal |last=Lefèvre |chapter=European Comics |pages=185–192 |editor-last=Booker |editor-first=M. Keith |title=Encyclopedia of Comic Books and Graphic Novels: [Two Volumes] |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YbkJ0QJrEZ8C |year=2010 |publisher=[[ABC-CLIO]] |isbn=978-0-313-35747-3}} | |||
* {{cite book |last1=Lyga |first1=Allyson A.W. |author1-link=Allyson Lyga |author2-link=Barry Lyga |last2=Lyga |first2=Barry |year=2004 |title=Graphic Novels in Your Media Center: A Definitive Guide |publisher=Libraries Unlimited |isbn=978-1-59158-142-0}}<!-- Lyga Lyga 2004 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=MacWilliams |first=Mark Wheeler |title=Japanese Visual Culture: Explorations in the World of Manga and Anime |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1eFnjcvxul4C |year=2008 |publisher=M.E. Sharpe |isbn=978-0-7656-1602-9}}<!-- MacWilliams 2008 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Mansfield |first=Stephen |title=Tokyo: A Cultural History |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Qrr-CKuAjkUC |year=2009 |publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |isbn=978-0-19-538634-9}}<!-- Mansfield 2009 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=McCloud |first=Scott |title=Understanding Comics: The Invisible Art |publisher=[[Kitchen Sink Press]] |year=1993 |isbn=978-0-87816-243-7}}<!-- McCloud 1993 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=McCloud |first=Scott |author-link=Scott McCloud |title=Reinventing Comics: How Imagination and Technology Are Revolutionizing an Art Form |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2RfNVk7PpnkC |year=2000 |publisher=[[HarperCollins]] |isbn=978-0-06-095350-8}}<!-- McCloud 2000 --> | |||
* {{cite book |editor-last=McKinney |editor-first=Mark |title=History and Politics in French-Language Comics and Graphic Novels |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XAMZ5AG0u4cC |year=2011 |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |isbn=978-1-60473-761-5}} | |||
* {{cite book |editor1-last=Meskin |editor1-first=Aaron |editor2-last=Cook |editor2-first=Roy T. |title=The Art of Comics: A Philosophical Approach |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KLzSI5V5-h8C&pg=PA13 |year=2012 |publisher=[[John Wiley & Sons]] |isbn=978-1-4443-3464-7}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Miller |first=Ann |author-link=Ann Miller (comics scholar) |chapter=Comic Strips/Cartoonists |title=Encyclopedia of Contemporary French Culture |editor1-last=Hughes |editor1-first=Alex |editor2-last=Reader |editor2-first=Keith |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=getDruRAaqgC&pg=PA116 |year=1998 |publisher=[[CRC Press]] |isbn=978-0-415-13186-5 |pages=[https://archive.org/details/encyclopediaofco0000unse_c6w0/page/116 116–119] |url=https://archive.org/details/encyclopediaofco0000unse_c6w0/page/116}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Miller |first=Ann |title=Reading Bande Dessinée: Critical Approaches to French-language Comic Strip |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=f5KY_CdALWkC |year=2007 |publisher=Intellect Books |isbn=978-1-84150-177-2}}<!-- Miller 2007 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Morita |first=Naoko |chapter=Cultural Recognition of Comics and Comics Studies: Comments on Thierry Groensteen's Keynote Lecture |pages=31–39 |title=Comics worlds & the world of comics : towards scholarship on a global scale |editor-last=Berndt |editor-first=Jaqueline |series=Global Manga Studies |volume=1 |publisher=International Manga Research Center, [[Kyoto Seika University]] |year=2010 |isbn=978-4-905187-03-5}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Nordling |first=Lee |title=Your Career in the Comics |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6BPuqsfKBGoC |year=1995 |publisher=[[Andrews McMeel Publishing]] |isbn=978-0-8362-0748-4}}<!-- Nordling 1995 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=O'Nale |first=Robert |chapter=Manga |pages=378–387 |editor-last=Booker |editor-first=M. Keith |title=Encyclopedia of Comic Books and Graphic Novels: [Two Volumes] |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YbkJ0QJrEZ8C |year=2010 |publisher=[[ABC-CLIO]] |isbn=978-0-313-35747-3}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Orr |first=Tamra |title=Manga Artists |url=https://archive.org/details/mangaartists0000orrt |url-access=registration |year=2008 |publisher=[[Rosen Publishing]] |isbn=978-1-4042-1854-3}}<!-- Orr 2008 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Petersen |first=Robert |title=Comics, Manga, and Graphic Novels: A History of Graphic Narratives |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=w1b5wVUEHpUC |year=2010 |publisher=[[ABC-CLIO]] |isbn=978-0-313-36330-6}}<!-- Petersen 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Poitras |first=Gilles |title=Anime Essentials: Every Thing a Fan Needs to Know |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wQ7JqkWjPNcC |year=2001 |publisher=Stone Bridge Press |isbn=978-1-880656-53-2}}<!-- Poitras 2001 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Power |first=Natsu Onoda |title=God of Comics: Osamu Tezuka and the Creation of Post-World War II Manga |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dvaR1-9HE7YC |year=2009 |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |isbn=978-1-60473-478-2}}<!-- Power 2009 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Raz |first=Aviad E. |title=Riding the Black Ship: Japan and Tokyo Disneyland |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7Jk9mv25eloC |year=1999 |publisher=[[Harvard University Asia Center]] |isbn=978-0-674-76894-9}}<!-- Raz 1999 --> | |||
* {{cite book |author-link=Shirrel Rhoades |last=Rhoades |first=Shirrel |title=A Complete History of American Comic Books |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=O16BXbITZwEC |year=2008 |publisher=[[Peter Lang (publisher)|Peter Lang]] |isbn=978-1-4331-0107-6}}<!-- Rhoades 2008 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Rowland |first=Barry D. |title=Herbie and Friends: Cartoons in Wartime |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=28GcLZAgLfkC |year=1990 |publisher=[[Dundurn Press]] |isbn=978-0-920474-52-5}}<!-- Rowland 1990 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Sabin |first=Roger |author-link=Roger Sabin |title=Adult Comics: An Introduction |publisher=[[Routledge]] |year=1993 |isbn=978-0-415-04419-6}}<!-- Sabin 1993 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Sabin |first=Roger |chapter=Some Observations on BD in the US |pages=175–188 |editor1-last=Forsdick |editor1-first=Charles |editor2-last=Grove |editor2-first=Laurence |editor3-last=McQuillan |editor3-first=Libbie |title=The Francophone Bande Dessinée |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lIdlzWpm7tQC |year=2005 |publisher=[[Rodopi (publisher)|Rodopi]] |isbn=978-90-420-1776-4}} | |||
* {{cite book |first=Mario |last=Saraceni |title=The Language of Comics |publisher=[[Routledge]] |year=2003 |url=https://www.questia.com/read/107985352 |isbn=978-0-415-21422-3}}<!-- Saraceni 2003 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Schodt |first=Frederik L. |title=Dreamland Japan: Writings on Modern Manga |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Loug6sbKTvEC |year=1996 |publisher=Stone Bridge Press |isbn=978-1-880656-23-5}}<!-- Schodt 1996 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Screech |first=Matthew |title=Masters of the Ninth Art: Bandes Dessinées and Franco-Belgian Identity |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EvkGQnWZf1gC |year=2005 |publisher=[[Liverpool University Press]] |isbn=978-0-85323-938-3}}<!-- Screech 2005 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Stewart |first=Ronald |chapter=Manga as Schism: Kitazawa Rakuten's Resistance to "Old-Fashioned" Japan |title=Manga's Cultural Crossroads |editor1-last=Berndt |editor1-first=Jaqueline |editor2-last=Kümmerling-Meibauer |editor2-first=Bettina |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=GdwJAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA27 |year=2014 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-134-10283-9 |pages=27–49}} | |||
* {{cite book |editor-last=Stringer |editor-first=Jenny |chapter=Graphic novel |title=The Oxford Companion to Twentieth-Century Literature in English |page=[https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780192122711/page/262 262] |publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-19-212271-1 |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780192122711/page/262}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Sugimoto |first=Yoshio |title=An Introduction to Japanese Society |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JyaeipnFbvUC |year=2010 |publisher=[[Cambridge University Press]] |isbn=978-0-521-87956-9}}<!-- Sugimoto 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Theobald |first=John |title=The Media and the Making of History |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=MiUcn_6DNF4C |year=2004 |publisher=Ashgate Publishing |isbn=978-0-7546-3822-3}}<!-- Theobald 2004 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Thomas |first=Evan |chapter=10: Invisible Art, Invisible Planes, Invisible People |title=Multicultural Comics: From Zap to Blue Beetle |editor-first=Frederick Luis |editor-last=Aldama |publisher=[[University of Texas Press]] |year=2010 |chapter-url=https://www.questia.com/read/120791130 |isbn=978-0-292-73743-3}}{{Dead link|date=December 2023|bot=InternetArchiveBot|fix-attempted=yes}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Thorne |first=Amy |chapter=Part Eight: Metacomic/Webcomics |title=Graphic Novels and Comics in Libraries and Archives: Essays on Readers, Research, History and Cataloging |editor-last=Weiner |editor-first=Robert G. |year=2010 |publisher=[[McFarland & Company]] |isbn=978-0-7864-5693-2 |pages=209–212}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Tondro |first=Jason |title=Superheroes of the Round Table: Comics Connections to Medieval and Renaissance Literature |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0QQD9ONH51UC |year=2011 |publisher=McFarland |isbn=978-0-7864-8876-6 |page=<!-- can't have both -->}} <!-- Tondro 2011 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Thompson |first=Jason |year=2007 |title=Manga: The Complete Guide |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=GvEFDD4rdWMC |location=New York |publisher=Ballantine Books |isbn=978-0-345-48590-8}} | |||
* {{cite book |last=Vessels |first=Joel E. |title=Drawing France: French Comics and the Republic |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Gut56lkOOfgC |year=2010 |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |isbn=978-1-60473-444-7}}<!-- Vessels 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last1=Williams |first1=Paul |last2=Lyons |first2=James |title=The Rise of the American Comics Artist: Creators and Contexts |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |year=2010 |isbn=978-1-60473-792-9}}<!-- Williams Lyons 2010 --> | |||
* {{cite book |last=Wong |first=Wendy Siuyi |title=Hong Kong Comics |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=sNaQQxhcD-oC |year=2002 |publisher=[[Princeton Architectural Press]] |isbn=978-1-56898-269-4}}<!-- Wong 2002 --> | |||
{{Refend}} | |||
====Academic journals==== | |||
{{Refbegin|colwidth=40em}} | |||
* {{cite journal |title=The Publication and Formats of Comics, Graphic Novels, and Tankobon |first=Chris |last=Couch |date=December 2000 |issn=1780-678X |journal=Image & Narrative |issue=1 |url=http://www.imageandnarrative.be/inarchive/narratology/chriscouch.htm |access-date=2012-02-05 |archive-date=2013-11-04 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131104223730/http://www.imageandnarrative.be/inarchive/narratology/chriscouch.htm |url-status=dead}} | |||
* {{cite journal |last=Frahm |first=Ole |title=Too much is too much. The never innocent laughter of the Comics. |date=October 2003 |issn=1780-678X |journal=Image & Narrative |issue=7 |url=http://www.imageandnarrative.be/inarchive/graphicnovel/olefrahm.htm |access-date=2012-02-05 |archive-date=2021-05-06 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210506155119/http://www.imageandnarrative.be/inarchive/graphicnovel/olefrahm.htm |url-status=dead}} | |||
* {{Cite journal |last1=Gomez Romero |first1=Luis |last2=Dahlman |first2=Ian |date=2012 |title=Introduction - Justice framed: law in comics and graphic novels |journal=Law Text Culture |volume=16 |issue=1 |pages=3–32 |url=https://ro.uow.edu.au/ltc/vol16/iss1/2}} | |||
* {{cite journal |last=Groensteen |first=Thierry |title=The Current State of French Comics Theory |journal=Scandinavian Journal of Comic Art |volume=1 |issue=1 |date=Spring 2012a |pages=111–122}} | |||
* {{cite journal |last=Cohen |first=Martin S. |title=The Novel in Woodcuts: A Handbook |journal=Journal of Modern Literature |volume=6 |issue=2 |date=April 1977 |pages=171–195 |jstor=3831165}} | |||
* {{cite journal |last=Yuan |first=Ting |title=From Ponyo to 'My Garfield Story': Using Digital Comics as an Alternative Pathway to Literary Composition |journal=Childhood Education |volume=87 |issue=4 |year=2011 |url=https://www.questia.com/read/1G1-254482672|archive-url=https://archive.today/20130411163409/http://www.questia.com/read/1G1-254482672|url-status=dead|archive-date=April 11, 2013}} | |||
{{Refend}} | |||
====Web==== | |||
{{Refbegin|colwidth=40em}} | |||
* {{cite web |first=Robert |last=Beerbohm |title=The Adventures of Obadiah Oldbuck Part III |work=The Search For Töpffer in America |url=http://scoop.diamondgalleries.com/Home/4/1/73/1017?articleID=43536 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130609004922/http://scoop.diamondgalleries.com/Home/4/1/73/1017?articleID=43536 |url-status=dead |archive-date=June 9, 2013 |year=2003 |access-date=2012-07-23}} | |||
* {{cite web |url=http://classic.tcj.com/top-stories/defining-comics-again-another-in-the-long-list-of-unnecessarily-complicated-definitions/ |title=Defining Comics Again: Another in the Long List of Unnecessarily Complicated Definitions |work=[[The Comics Journal]] |publisher=[[Fantagraphics Books]] |author-link=R. C. Harvey |first=R. C. |last=Harvey |date=2010-12-20 |access-date=2013-02-06 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110914065411/http://classic.tcj.com/top-stories/defining-comics-again-another-in-the-long-list-of-unnecessarily-complicated-definitions/ |archive-date=2011-09-14 |url-status=dead}} | |||
* {{cite web |url=http://www.toonopedia.com/glossary.htm |archive-url=http://arquivo.pt/wayback/20091016112147/http://www.toonopedia.com/glossary.htm |archive-date=2009-10-16 |url-status=dead |access-date=2013-02-05 |first=Don |last=Markstein |work=[[Don Markstein's Toonopedia]] |year=2010 |title=Glossary of Specialized Cartoon-related Words and Phrases Used in Don Markstein's Toonopedia}} | |||
{{Refend}} | |||
==Further reading== | |||
{{Refbegin|30em}} | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |author-link=David Carrier |first=David |last=Carrier |title=The Aesthetics of Comics |publisher=Penn State Press |year=2002 |isbn=978-0-271-02188-1}}<!-- Carrier 2002 --> | |||
* {{Cite book |ref=none |isbn=978-1-4411-8145-9 |title=The Visual Language of Comics: Introduction to the Structure and Cognition of Sequential Images |last1=Cohn |first1=Neil |year=2013 |publisher=Bloomsbury |location=London |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RVABAQAAQBAJ&q=the+visual+language+of+comics}}<!-- Cohn 2013 --> | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |last1=Dowd |first1=Douglas Bevan |last2=Hignite |first2=Todd |title=Strips, Toons, And Bluesies: Essays in Comics And Culture |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TjzlxyfWbxwC |year=2006 |publisher=Princeton Architectural Press |isbn=978-1-56898-621-0}}<!-- Dowd Hignite 2006 --> | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |author-link=Will Eisner |first=Will |last=Eisner |title=Graphic Storytelling |publisher=Poorhouse Press |year=1995 |isbn=978-0-9614728-3-2}}<!-- Eisner 1995 --> | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |last=Estren |first=Mark James |title=A History of Underground Comics |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hQb_q6DWle4C |year=1993 |publisher=Ronin Publishing |isbn=978-0-914171-64-5}}<!-- Estren 1993 --> | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |last=Groensteen |first=Thierry |title=The System of Comics |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=tgNKwRM00w0C |year=2007 |orig-year=1999 |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |isbn=978-1-57806-925-5}}<!-- Groensteen 2007 --> | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |editor1-link=Gary Groth |editor1-first=Gary |editor1-last=Groth |editor2-first=R. |editor2-last=Fiore |title=The New Comics |publisher=[[Berkley Books]] |year=1988 |isbn=978-0-425-11366-0}} | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |editor1-last=Heer |editor1-first=Jeet |editor2-last=Worcester |editor2-first=Kent |title=A Comics Studies Reader |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EjzAZtoxfx8C |year=2012 |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |isbn=978-1-60473-109-5}} | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |editor-link=Maurice Horn |editor-first=Maurice |editor-last=Horn |title=The World Encyclopedia of Comics |publisher=[[Avon (publisher)|Avon]] |year=1977 |isbn=978-0-87754-323-7}} | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |last=Kunzle |first=David |title=The Early Comic Strip: Narrative Strips and Picture Stories in the European Broadsheet from c. 1450 to 1825 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yVY8PgAACAAJ |year=1973 |publisher=[[University of California Press]] |isbn=978-0-520-05775-3 |oclc=470776042}}<!-- Kunzle 1973 --> | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |last=Kunzle |first=David |title=History of the Comic Strip: The Nineteenth Century |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IAhTJO_R7eoC |year=1990 |publisher=[[University of California Press]] |isbn=978-0-520-01865-5}}<!-- Kunzle 1990 --> | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |last1=McCloud |first1=Scott |title=Reinventing Comics: How Tmagination and Technology are Revolutionizing an Art Form |date=2000 |publisher=Perennial |isbn=0060953500 |edition=1st Perennial}} | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |last1=McCloud |first1=Scott |title=Making Comics: Storytelling Secrets of Comics, Manga and Graphic Novels |url=https://archive.org/details/makingcomicsstor0000mccl |url-access=registration |date=2006 |publisher=HarperCollins |isbn=0060780940 |edition=1st Perennial}} | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |author-link=Roger Sabin |first=Roger |last=Sabin |title=Comics, Comix and Graphic Novels: A History of Comic Art |publisher=Phaidon |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-7148-3993-6}}<!-- Sabin 1996 --> | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |editor1-first=Daniel |editor1-last=Stein |editor2-first=Jan-Noël |editor2-last=Thon |title=From Comic Strips to Graphic Novels. Contributions to the Theory and History of Graphic Narrative |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3RisCAAAQBAJ&q=from+comic+strips+to+graphic+novels |publisher=[[De Gruyter]] |year=2015 |isbn=978-3-11-042656-4}} | |||
* {{cite book |ref=none |author-link=Coulton Waugh |first=Coulton |last=Waugh |title=The Comics |publisher=[[University Press of Mississippi]] |year=1947 |isbn=978-0-87805-499-2}}<!-- Waugh 1947 --> | |||
{{Refend}} | |||
==External links== | |||
{{Sister project links}} | |||
'''Academic journals''' | |||
* [http://www.comicsgrid.com/ ''The Comics Grid: Journal of Comics Scholarship''] | |||
* [http://www.english.ufl.edu/imagetext/ ''ImageTexT: Interdisciplinary Comics Studies''] | |||
* [http://www.imageandnarrative.be/ ''Image <nowiki>[&]</nowiki> Narrative''] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201106235640/http://www.imageandnarrative.be/ |date=2020-11-06 }} | |||
* [http://www.ijoca.com/ International ''Journal of Comic Art''] | |||
* [http://www.tandfonline.com/toc/rcom20/current ''Journal of Graphic Novels and Comics''] | |||
'''Archives''' | |||
* [http://cartoons.osu.edu/ Billy Ireland Cartoon Library & Museum] | |||
* [http://comics.lib.msu.edu/ Michigan State University Comic Art Collection] | |||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20110719050622/http://mulibraries.missouri.edu/specialcollections/comic.htm Comic Art Collection] at the [[University of Missouri]] | |||
* [http://www.cartoonart.org/ Cartoon Art Museum of San Francisco] | |||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20130823023710/http://www.time.com/time/archive/collections/0,21428,c_comics,00.shtml ''Time'' Archives' Collection of Comics] | |||
* {{cite web | |||
|work = Prints & Books | |||
|publisher = [[Victoria and Albert Museum]] | |||
|url = http://www.vam.ac.uk/collections/prints_books/features/comics/index.html | |||
|title = Comics in the National Art Library | |||
|access-date = 2011-03-15 | |||
|url-status = dead | |||
|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20091104235741/http://www.vam.ac.uk/collections/prints_books/features/comics/index.html | |||
|archive-date = 2009-11-04 | |||
}} | |||
'''Databases''' | |||
* [http://comics.org/ Grand Comics Database] | |||
{{Comics}} | |||
{{Portal bar|Comics|Arts|Visual arts}} | |||
{{Authority control}} | |||
[[Category:Comics| ]] | |||
[[Category:Narrative forms]] | |||
Revision as of 22:09, 16 December 2024
Template:Short description Template:Redirect Template:Redirect Template:Good article Template:Use shortened footnotes

Template:Not a typo a medium used to express ideas with images, often combined with text or other visual information. It typically Template:Not a typo the form of a sequence of panels of images. Textual devices such as speech balloons, captions, and onomatopoeia can indicate dialogue, narration, sound effects, or other information. There is no consensus among theorists and historians on a definition of comics; some emphasize the combination of images and text, some sequentiality or other image relations, and others historical aspects such as mass reproduction or the use of recurring characters. Cartooning and other forms of illustration are the most common means of image-making in comics. Photo comics is a form that uses photographic images. Common forms include comic strips, editorial and gag cartoons, and comic books. Since the late 20th century, bound volumes such as graphic novels, comic albums, and Template:Transl have become increasingly common, along with webcomics as well as scientific/medical comics.[1]
The history of comics has followed different paths in different cultures. Scholars have posited a pre-history as far back as the Lascaux cave paintings. By the mid-20th century, comics flourished, particularly in the United States, western Europe (especially France and Belgium), and Japan. The history of European comics is often traced to Rodolphe Töpffer's cartoon strips of the 1830s, while Wilhelm Busch and his Max and Moritz also had a global impact from 1865 on,[2][3][4][5] and became popular following the success in the 1930s of strips and books such as The Adventures of Tintin. American comics emerged as a mass medium in the early 20th century with the advent of newspaper comic strips; magazine-style comic books followed in the 1930s, the superhero genre became prominent after Superman appeared in 1938. Histories of Japanese comics and cartooning (Template:Transl) propose origins as early as the 12th century. Japanese comics are generally held separate from the evolution of Euro-American comics, and Western comic art probably originated in 17th-century Italy.[6] Modern Japanese comic strips emerged in the early 20th century, and the output of comic magazines and books rapidly expanded in the post-World War II era (1945)– with the popularity of cartoonists such as Osamu Tezuka. Template:Not a typo had a lowbrow reputation for much of their history, but towards the end of the 20th century, they began to find greater acceptance with the public and academics.
The English term comics is used as a singular noun when it refers to the medium itself (e.g. "Comics is a visual art form."), but becomes plural when referring to works collectively (e.g. "Comics are popular reading material.").Template:TOC limit
The comics may be further adapted to animations (anime), dramas, TV shows, movies.
Origins and traditions
- Examples of early comics
The European, American, and Japanese comics traditions have followed different paths. Europeans have seen their tradition as beginning with the Swiss Rodolphe Töpffer from as early as 1469 and Americans have seen the origin of theirs in Richard F. Outcault's 1890s newspaper strip The Yellow Kid, though many Americans have come to recognize Töpffer's precedence. Wilhelm Busch directly influenced Rudolph Dirks and his Katzenjammer Kids.[7][8][9][10]Template:Sfnm Japan has a long history of satirical cartoons and comics leading up to the World War II era. The ukiyo-e artist Hokusai popularized the Japanese term for comics and cartooning, Template:Transl, in the early 19th century.Template:Sfnm In the 1930s Harry "A" Chesler started a comics studio, which eventually at its height employed 40 artists working for 50 different publishers who helped make the comics medium flourish in "the Golden Age of Comics" after World War II.[11] In the post-war era modern Japanese comics began to flourish when Osamu Tezuka produced a prolific body of work.Template:Sfnm Towards the close of the 20th century, these three traditions converged in a trend towards book-length comics: the comic album in Europe, the Template:TranslTemplate:Efn in Japan, and the graphic novel in the English-speaking countries.
Outside of these genealogies, comics theorists and historians have seen precedents for comics in the Lascaux cave paintingsTemplate:Sfnm in France (some of which appear to be chronological sequences of images), Egyptian hieroglyphs, Trajan's Column in Rome, the 11th-century Norman Bayeux Tapestry,Template:Sfnm the 1370 Template:Lang woodcut, the 15th-century Template:Lang and block books, Michelangelo's The Last Judgment in the Sistine Chapel, and William Hogarth's 18th-century sequential engravings, amongst others.Template:Efn
English-language comics

Template:Multiple image Template:Main
Illustrated humour periodicals were popular in 19th-century Britain, the earliest of which was the short-lived The Glasgow Looking Glass in 1825.[12] The most popular was Punch, which popularized the term cartoon for its humorous caricatures. On occasion the cartoons in these magazines appeared in sequences; the character Ally Sloper featured in the earliest serialized comic strip when the character began to feature in its own weekly magazine in 1884.
American comics developed out of such magazines as Puck, Judge, and Life. The success of illustrated humour supplements in the New York World and later the New York American, particularly Outcault's The Yellow Kid, led to the development of newspaper comic strips. Early Sunday strips were full-page and often in colour. Between 1896 and 1901 cartoonists experimented with sequentiality, movement, and speech balloons. An example is Gustave Verbeek, who wrote his comic series "The UpsideDowns of Old Man Muffaroo and Little Lady Lovekins" between 1903 and 1905. These comics were made in such a way that one could read the 6-panel comic, flip the book and keep reading. He made 64 such comics in total. In 2012, a remake of a selection of the comics was made by Marcus Ivarsson in the book 'In Uppåner med Lilla Lisen & Gamle Muppen'. ()
Shorter, black-and-white daily strips began to appear early in the 20th century, and became established in newspapers after the success in 1907 of Bud Fisher's Mutt and Jeff. In Britain, the Amalgamated Press established a popular style of a sequence of images with text beneath them, including Illustrated Chips and Comic Cuts. Humour strips predominated at first, and in the 1920s and 1930s strips with continuing stories in genres such as adventure and drama also became popular.
Thin periodicals called comic books appeared in the 1930s, at first reprinting newspaper comic strips; by the end of the decade, original content began to dominate. The success in 1938 of Action Comics and its lead hero Superman marked the beginning of the Golden Age of Comic Books, in which the superhero genre was prominent. In the UK and the Commonwealth, the DC Thomson-created Dandy (1937) and Beano (1938) became successful humor-based titles, with a combined circulation of over 2 million copies by the 1950s. Their characters, including "Dennis the Menace", "Desperate Dan" and "The Bash Street Kids" have been read by generations of British children. The comics originally experimented with superheroes and action stories before settling on humorous strips featuring a mix of the Amalgamated Press and US comic book styles.

The popularity of superhero comic books declined in the years following World War II, while comic book sales continued to increase as other genres proliferated, such as romance, westerns, crime, horror, and humour. Following a sales peak in the early 1950s, the content of comic books (particularly crime and horror) was subjected to scrutiny from parent groups and government agencies, which culminated in Senate hearings that led to the establishment of the Comics Code Authority self-censoring body. The Code has been blamed for stunting the growth of American comics and maintaining its low status in American society for much of the remainder of the century. Superheroes re-established themselves as the most prominent comic book genre by the early 1960s. Underground comix challenged the Code and readers with adult, countercultural content in the late 1960s and early 1970s. The underground gave birth to the alternative comics movement in the 1980s and its mature, often experimental content in non-superhero genres.Template:Sfnm
Comics in the US has had a lowbrow reputation stemming from its roots in mass culture; cultural elites sometimes saw popular culture as threatening culture and society. In the latter half of the 20th century, popular culture won greater acceptance, and the lines between high and low culture began to blur. Comics nevertheless continued to be stigmatized, as the medium was seen as entertainment for children and illiterates.
The graphic novel—book-length comics—began to gain attention after Will Eisner popularized the term with his book A Contract with God (1978). The term became widely known with the public after the commercial success of Maus, Watchmen, and The Dark Knight Returns in the mid-1980s.Template:Sfnm In the 21st century graphic novels became established in mainstream bookstores and libraries and webcomics became common.
Franco-Belgian and European comics
The francophone Swiss Rodolphe Töpffer produced comic strips beginning in 1827, and published theories behind the form. Wilhelm Busch first published his Max and Moritz in 1865.[13] Cartoons appeared widely in newspapers and magazines from the 19th century. The success of Zig et Puce in 1925 popularized the use of speech balloons in European comics, after which Franco-Belgian comics began to dominate.Template:Sfnm The Adventures of Tintin, with its signature clear line style,Template:Sfnm was first serialized in newspaper comics supplements beginning in 1929, and became an icon of Franco-Belgian comics.Template:Sfnm
Following the success of Template:Lang (est. 1934), dedicated comics magazinesTemplate:Sfnm like Spirou (est. 1938) and Tintin (1946–1993), and full-colour comic albums became the primary outlet for comics in the mid-20th century. As in the US, at the time comics were seen as infantile and a threat to culture and literacy; commentators stated that "none bear up to the slightest serious analysis",Template:Efn and that comics were "the sabotage of all art and all literature".Template:Efn
In the 1960s, the term Template:Lang ("drawn strips") came into wide use in French to denote the medium. Cartoonists began creating comics for mature audiences,Template:Sfnm and the term "Ninth Art"Template:Efn was coined, as comics began to attract public and academic attention as an artform. A group including René Goscinny and Albert Uderzo founded the magazine Pilote in 1959 to give artists greater freedom over their work. Goscinny and Uderzo's The Adventures of Asterix appeared in it and went on to become the best-selling French-language comics series. From 1960, the satirical and taboo-breaking Hara-Kiri defied censorship laws in the countercultural spirit that led to the May 1968 events.
Frustration with censorship and editorial interference led to a group of Pilote cartoonists to found the adults-only L'Écho des savanes in 1972. Adult-oriented and experimental comics flourished in the 1970s, such as in the experimental science fiction of Mœbius and others in Métal hurlant, even mainstream publishers took to publishing prestige-format adult comics.
From the 1980s, mainstream sensibilities were reasserted and serialization became less common as the number of comics magazines decreased and many comics began to be published directly as albums. Smaller publishers such as L'Association that published longer works in non-traditional formats by auteur-istic creators also became common. Since the 1990s, mergers resulted in fewer large publishers, while smaller publishers proliferated. Sales overall continued to grow despite the trend towards a shrinking print market.
Japanese comics

Japanese comics and cartooning (Template:Transl),Template:Efn have a history that has been seen as far back as the anthropomorphic characters in the 12th-to-13th-century Template:Transl, 17th-century Template:Transl and Template:Transl picture books, and woodblock prints such as ukiyo-e which were popular between the 17th and 20th centuries. The Template:Transl contained examples of sequential images, movement lines, and sound effects.
Illustrated magazines for Western expatriates introduced Western-style satirical cartoons to Japan in the late 19th century. New publications in both the Western and Japanese styles became popular, and at the end of the 1890s, American-style newspaper comics supplements began to appear in Japan, as well as some American comic strips. 1900 saw the debut of the Jiji Manga in the Jiji Shinpō newspaper—the first use of the word "manga" in its modern sense, and where, in 1902, Rakuten Kitazawa began the first modern Japanese comic strip.Template:Sfnm By the 1930s, comic strips were serialized in large-circulation monthly girls' and boys' magazine and collected into hardback volumes.Template:Sfnm
The modern era of comics in Japan began after World War II, propelled by the success of the serialized comics of the prolific Osamu Tezuka and the comic strip Sazae-san.Template:Sfnm Genres and audiences diversified over the following decades. Stories are usually first serialized in magazines which are often hundreds of pages thick and may contain over a dozen stories;Template:Sfnm they are later compiled in Template:Transl-format books. At the turn of the 20th and 21st centuries, nearly a quarter of all printed material in Japan was comics.Template:Sfnm Translations became extremely popular in foreign markets—in some cases equaling or surpassing the sales of domestic comics.
Forms and formats
Comic strips are generally short, multipanel comics that have, since the early 20th century, most commonly appeared in newspapers. In the US, daily strips have normally occupied a single tier, while Sunday strips have been given multiple tiers. Since the early 20th century, daily newspaper comic strips have typically been printed in black-and-white and Sunday comics have usually been printed in colour and have often occupied a full newspaper page.
Specialized comics periodicals formats vary greatly in different cultures. Comic books, primarily an American format, are thin periodicalsTemplate:Sfnm usually published in colour. European and Japanese comics are frequently serialized in magazines—monthly or weekly in Europe, and usually black-and-white and weekly in Japan.Template:Sfnm Japanese comics magazine typically run to hundreds of pages.
Book-length comics take different forms in different cultures. European comic albums are most commonly colour volumes printed at A4-size, a larger page size than used in many other cultures.Template:Sfnm In English-speaking countries, the trade paperback format originating from collected comic books have also been chosen for original material. Otherwise, bound volumes of comics are called graphic novels and are available in various formats. Despite incorporating the term "novel"—a term normally associated with fiction—"graphic novel" also refers to non-fiction and collections of short works.Template:Sfnm Japanese comics are collected in volumes called Template:Lang following magazine serialization.
Gag and editorial cartoons usually consist of a single panel, often incorporating a caption or speech balloon. Definitions of comics which emphasize sequence usually exclude gag, editorial, and other single-panel cartoons; they can be included in definitions that emphasize the combination of word and image. Gag cartoons first began to proliferate in broadsheets published in Europe in the 18th and 19th centuries, and the term "cartoon"Template:Efn was first used to describe them in 1843 in the British humour magazine Punch.
Webcomics are comics that are available on the internet, first being published the 1980s. They are able to potentially reach large audiences, and new readers can often access archives of previous installments. Webcomics can make use of an infinite canvas, meaning they are not constrained by the size or dimensions of a printed comics page.Template:Sfnm
Some consider storyboards and wordless novels to be comics. Film studios, especially in animation, often use sequences of images as guides for film sequences. These storyboards are not intended as an end product and are rarely seen by the public. Wordless novels are books which use sequences of captionless images to deliver a narrative.
Comics studies
Similar to the problems of defining literature and film, no consensus has been reached on a definition of the comics medium, and attempted definitions and descriptions have fallen prey to numerous exceptions. Theorists such as Töpffer, R. C. Harvey, Will Eisner, David Carrier, Alain Rey, and Lawrence Grove emphasize the combination of text and images, though there are prominent examples of pantomime comics throughout its history. Other critics, such as Thierry Groensteen and Scott McCloud, have emphasized the primacy of sequences of images. Towards the close of the 20th century, different cultures' discoveries of each other's comics traditions, the rediscovery of forgotten early comics forms, and the rise of new forms made defining comics a more complicated task.
European comics studies began with Töpffer's theories of his own work in the 1840s, which emphasized panel transitions and the visual–verbal combination. No further progress was made until the 1970s. Pierre Fresnault-Deruelle then took a semiotics approach to the study of comics, analyzing text–image relations, page-level image relations, and image discontinuities, or what Scott McCloud later dubbed "closure". In 1987, Henri Vanlier introduced the term Template:Lang, or "multiframe", to refer to the comics page as a semantic unit. By the 1990s, theorists such as Benoît Peeters and Thierry Groensteen turned attention to artists' poïetic creative choices. Thierry Smolderen and Harry Morgan have held relativistic views of the definition of comics, a medium that has taken various, equally valid forms over its history. Morgan sees comics as a subset of "Template:Lang" (or "drawn literatures"). French theory has come to give special attention to the page, in distinction from American theories such as McCloud's which focus on panel-to-panel transitions. In the mid-2000s, Neil Cohn began analyzing how comics are understood using tools from cognitive science, extending beyond theory by using actual psychological and neuroscience experiments. This work has argued that sequential images and page layouts both use separate rule-bound "grammars" to be understood that extend beyond panel-to-panel transitions and categorical distinctions of types of layouts, and that the brain's comprehension of comics is similar to comprehending other domains, such as language and music.
Historical narratives of manga tend to focus either on its recent, post-WWII history, or on attempts to demonstrate deep roots in the past, such as to the Template:Transl picture scroll of the 12th and 13th centuries, or the early 19th-century Hokusai Manga. The first historical overview of Japanese comics was Seiki Hosokibara's Template:TranslTemplate:Efn in 1924.Template:Sfnm Early post-war Japanese criticism was mostly of a left-wing political nature until the 1986 publication of Tomofusa Kure's Modern Manga: The Complete Picture,Template:Efn which de-emphasized politics in favour of formal aspects, such as structure and a "grammar" of comics. The field of Template:Transl studies increased rapidly, with numerous books on the subject appearing in the 1990s. Formal theories of Template:Transl have focused on developing a "manga expression theory",Template:Efn with emphasis on spatial relationships in the structure of images on the page, distinguishing the medium from film or literature, in which the flow of time is the basic organizing element. Comics studies courses have proliferated at Japanese universities, and Japan Society for Studies in Cartoon and Comics Template:SmallTemplate:Efn was established in 2001 to promote comics scholarship. The publication of Frederik L. Schodt's Manga! Manga! The World of Japanese Comics in 1983 led to the spread of use of the word manga outside Japan to mean "Japanese comics" or "Japanese-style comics".
Coulton Waugh attempted the first comprehensive history of American comics with The Comics (1947). Will Eisner's Comics and Sequential Art (1985) and Scott McCloud's Understanding Comics (1993) were early attempts in English to formalize the study of comics. David Carrier's The Aesthetics of Comics (2000) was the first full-length treatment of comics from a philosophical perspective. Prominent American attempts at definitions of comics include Eisner's, McCloud's, and Harvey's. Eisner described what he called "sequential art" as "the arrangement of pictures or images and words to narrate a story or dramatize an idea";Template:Sfnm Scott McCloud defined comics as "juxtaposed pictorial and other images in deliberate sequence, intended to convey information and/or to produce an aesthetic response in the viewer",Template:Sfnm a strictly formal definition which detached comics from its historical and cultural trappings. R. C. Harvey defined comics as "pictorial narratives or expositions in which words (often lettered into the picture area within speech balloons) usually contribute to the meaning of the pictures and vice versa".Template:Sfnm Each definition has had its detractors. Harvey saw McCloud's definition as excluding single-panel cartoons, and objected to McCloud's de-emphasizing verbal elements, insisting "the essential characteristic of comics is the incorporation of verbal content". Aaron Meskin saw McCloud's theories as an artificial attempt to legitimize the place of comics in art history.
Cross-cultural study of comics is complicated by the great difference in meaning and scope of the words for "comics" in different languages. The French term for comics, Template:Lang ("drawn strip") emphasizes the juxtaposition of drawn images as a defining factor,Template:Sfnm which can imply the exclusion of even photographic comics. The term Template:Transl is used in Japanese to indicate all forms of comics, cartooning, and caricature.
Terminology
The term comics refers to the comics medium when used as an uncountable noun and thus takes the singular: "comics is a medium" rather than "comics are a medium". When comic appears as a countable noun it refers to instances of the medium, such as individual comic strips or comic books: "Tom's comics are in the basement."Template:Sfnm
Panels are individual images containing a segment of action, often surrounded by a border. Prime moments in a narrative are broken down into panels via a process called encapsulation. The reader puts the pieces together via the process of closure by using background knowledge and an understanding of panel relations to combine panels mentally into events. The size, shape, and arrangement of panels each affect the timing and pacing of the narrative. The contents of a panel may be asynchronous, with events depicted in the same image not necessarily occurring at the same time.Template:Sfnm

Text is frequently incorporated into comics via speech balloons, captions, and sound effects. Speech balloons indicate dialogue (or thought, in the case of thought balloons), with tails pointing at their respective speakers.Template:Sfnm Captions can give voice to a narrator, convey characters' dialogue or thoughts,Template:Sfnm or indicate place or time.Template:Sfnm Speech balloons themselves are strongly associated with comics, such that the addition of one to an image is sufficient to turn the image into comics. Sound effects mimic non-vocal sounds textually using onomatopoeia sound-words.
Cartooning is most frequently used in making comics, traditionally using ink (especially India ink) with dip pens or ink brushes;Template:Sfnm mixed media and digital technology have become common. Cartooning techniques such as motion linesTemplate:Sfnm and abstract symbols are often employed.Template:Sfnm
While comics are often the work of a single creator, the labour of making them is frequently divided between a number of specialists. There may be separate writers and artists, and artists may specialize in parts of the artwork such as characters or backgrounds, as is common in Japan. Particularly in American superhero comic books, the art may be divided between a penciller, who lays out the artwork in pencil; an inker, who finishes the artwork in ink;Template:Sfnm a colourist; and a letterer, who adds the captions and speech balloons.
Etymology
The English-language term comics derives from the humorous (or "comic") work which predominated in early American newspaper comic strips, but usage of the term has become standard for non-humorous works as well. The alternate spelling comix – coined by the underground comix movement – is sometimes used to address such ambiguities. The term "comic book" has a similarly confusing history since they are most often not humorous and are periodicals, not regular books. It is common in English to refer to the comics of different cultures by the terms used in their languages, such as Template:Transl for Japanese comics, or Template:Lang for French-language Franco-Belgian comics.
Many cultures have taken their word for comics from English, including Russian (Template:Lang, Template:Transl) and German (Template:Lang). Similarly, the Chinese term Template:TranslTemplate:Sfnm and the Korean Template:Transl derive from the Chinese characters with which the Japanese term Template:Transl is written.Template:Sfnm
See also
See also lists
- List of best-selling comic series
- List of best-selling manga
- List of comic books
- List of comics by country
- List of comics creators
- List of comics publishing companies
- List of comic strip syndicates
- List of Franco-Belgian comics series
- List of newspaper comic strips
- Lists of manga
- List of manga artists
- List of manga magazines
- List of manga publishers
- List of years in comics
Notes
References
Works cited
Books
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite bookTemplate:Dead link
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
Academic journals
- Template:Cite journal
- Template:Cite journal
- Template:Cite journal
- Template:Cite journal
- Template:Cite journal
- Template:Cite journal
Web
Further reading
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
- Template:Cite book
External links
Academic journals
- The Comics Grid: Journal of Comics Scholarship
- ImageTexT: Interdisciplinary Comics Studies
- Image [&] Narrative Template:Webarchive
- International Journal of Comic Art
- Journal of Graphic Novels and Comics
Archives
- Billy Ireland Cartoon Library & Museum
- Michigan State University Comic Art Collection
- Comic Art Collection at the University of Missouri
- Cartoon Art Museum of San Francisco
- Time Archives' Collection of Comics
- Template:Cite web
Databases
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Gothic in Comics and Graphic Novels by Julia Round page 24 and 25
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite news
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web